Involvement of microglia activation in the lead induced long-term potentiation impairment
- PMID: 22952811
- PMCID: PMC3432044
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043924
Involvement of microglia activation in the lead induced long-term potentiation impairment
Abstract
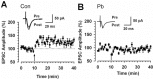
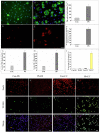
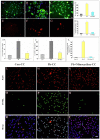
Exposure of Lead (Pb), a known neurotoxicant, can impair spatial learning and memory probably via impairing the hippocampal long-term potentiation (LTP) as well as hippocampal neuronal injury. Activation of hippocampal microglia also impairs spatial learning and memory. Thus, we raised the hypothesis that activation of microglia is involved in the Pb exposure induced hippocampal LTP impairment and neuronal injury. To test this hypothesis and clarify its underlying mechanisms, we investigated the Pb-exposure on the microglia activation, cytokine release, hippocampal LTP level as well as neuronal injury in in vivo or in vitro model. The changes of these parameters were also observed after pretreatment with minocycline, a microglia activation inhibitor. Long-term low dose Pb exposure (100 ppm for 8 weeks) caused significant reduction of LTP in acute slice preparations, meanwhile, such treatment also significantly increased hippocampal microglia activation as well as neuronal injury. In vitro Pb-exposure also induced significantly increase of microglia activation, up-regulate the release of cytokines including tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) in microglia culture alone as well as neuronal injury in the co-culture with hippocampal neurons. Inhibiting the microglia activation with minocycline significantly reversed the above-mentioned Pb-exposure induced changes. Our results showed that Pb can cause microglia activation, which can up-regulate the level of IL-1β, TNF-α and iNOS, these proinflammatory factors may cause hippocampal neuronal injury as well as LTP deficits.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Bellinger DC (2004) Lead. Pediatrics 113: 1016–22. - PubMed
-
- Finkelstein Y, Markowitz ME, Rosen JF (1998) Low-level lead-induced neurotoxicity in children: an update on central nervous system effects. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 27: 168–76. - PubMed
-
- Rosen JF (1995) Adverse health effects of lead at low exposure levels: trends in the management of childhood lead poisoning. Toxicology 97: 11–7. - PubMed
-
- Needleman HL, McFarland C, Ness RB, Fienberg SE, Tobin MJ (2002) Bone lead levels in adjudicated delinquents. A case control study. Neurotoxicol Teratol 24: 711–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

