StarD7 knockdown modulates ABCG2 expression, cell migration, proliferation, and differentiation of human choriocarcinoma JEG-3 cells
- PMID: 22952907
- PMCID: PMC3430668
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044152
StarD7 knockdown modulates ABCG2 expression, cell migration, proliferation, and differentiation of human choriocarcinoma JEG-3 cells
Abstract
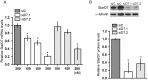
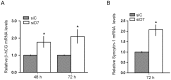
Background: StAR-related lipid transfer domain containing 7 (StarD7) is a member of the START-domain protein family whose function still remains unclear. Our data from an explorative microarray assay performed with mRNAs from StarD7 siRNA-transfected JEG-3 cells indicated that ABCG2 (ATP-binding cassette sub-family G member 2) was one of the most abundantly downregulated mRNAs.
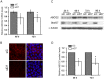
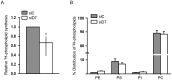
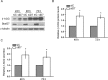
Methodology/principal findings: Here, we have confirmed that knocking down StarD7 mRNA lead to a decrease in the xenobiotic/lipid transporter ABCG2 at both the mRNA and protein levels (-26.4% and -41%, p<0.05, at 48 h of culture, respectively). Also a concomitant reduction in phospholipid synthesis, bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) uptake and (3)H-thymidine incorporation was detected. Wound healing and transwell assays revealed that JEG-3 cell migration was significantly diminished (p<0.05). Conversely, biochemical differentiation markers such as human chorionic gonadotrophin β-subunit (βhCG) protein synthesis and secretion as well as βhCG and syncytin-1 mRNAs were increased approximately 2-fold. In addition, desmoplakin immunostaining suggested that there was a reduction of intercellular desmosomes between adjacent JEG-3 cells after knocking down StarD7.
Conclusions/significance: Altogether these findings provide evidence for a role of StarD7 in cell physiology indicating that StarD7 modulates ABCG2 multidrug transporter level, cell migration, proliferation, and biochemical and morphological differentiation marker expression in a human trophoblast cell model.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Ponting CP, Aravind L (1999) START: a lipid-binding domain in StAR, HD-ZIP and signalling proteins. Trends Biochem Sci 24: 130–132. - PubMed
-
- Tsujishita Y, Hurley JH (2000) Structure and lipid transport mechanism of a StAR-related domain. Nat Struct Biol 7: 408–414. - PubMed
-
- Clark BJ (2011) The mammalian START domain protein family in lipid transport in health and disease. J Endocrinol 212(3): 257–275. - PubMed
-
- Durand S, Angeletti S, Genti-Raimondi S (2004) GTT1/StarD7, a novel phosphatidylcholine transfer protein-like highly expressed in gestational trophoblastic tumour: cloning and characterization. Placenta 25: 37–44. - PubMed
-
- Angeletti S, Rena V, Nores R, Fretes R, Panzetta-Dutari GM, et al. (2008) Expression and localization of StarD7 in trophoblast cells. Placenta 29: 396–404. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

