Adaptive ridge regression for rare variant detection
- PMID: 22952918
- PMCID: PMC3429469
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044173
Adaptive ridge regression for rare variant detection
Abstract
It is widely believed that both common and rare variants contribute to the risks of common diseases or complex traits and the cumulative effects of multiple rare variants can explain a significant proportion of trait variances. Advances in high-throughput DNA sequencing technologies allow us to genotype rare causal variants and investigate the effects of such rare variants on complex traits. We developed an adaptive ridge regression method to analyze the collective effects of multiple variants in the same gene or the same functional unit. Our model focuses on continuous trait and incorporates covariate factors to remove potential confounding effects. The proposed method estimates and tests multiple rare variants collectively but does not depend on the assumption of same direction of each rare variant effect. Compared with the Bayesian hierarchical generalized linear model approach, the state-of-the-art method of rare variant detection, the proposed new method is easy to implement, yet it has higher statistical power. Application of the new method is demonstrated using the well-known data from the Dallas Heart Study.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
 .
.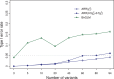
 and
and  criteria (
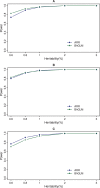
criteria ( ).
).
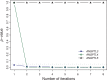
 distribution.
distribution.References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

