SHP-1 phosphatase is a critical regulator in preventing natural killer cell self-killing
- PMID: 22952938
- PMCID: PMC3432062
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044244
SHP-1 phosphatase is a critical regulator in preventing natural killer cell self-killing
Abstract
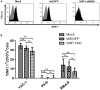
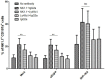
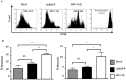
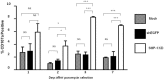
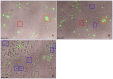
Balance of signals generated from the engaged activating and inhibitory surface receptors regulates mature NK cell activities. The inhibitory receptors signal through immunoreceptor tyrosine based inhibitory motifs (ITIM), and recruit phosphatases such as SHP-1 to inhibit NK cell activation. To directly examine the importance of SHP-1 in regulating activities and cell fate of mature NK cells, we used our established lentiviral-based engineering protocol to knock down the SHP-1 protein expression in primary C57BL/6NCrl cells. Gene silencing of the SHP-1 in primary NK cells abrogated the ability of ITIM-containing NK inhibitory receptors to suppress the activation signals induced by NK1.1 activating receptors. We followed the fates of stably transduced SHP-1 silenced primary NK cells over a longer period of time in IL-2 containing cultures. We observed an impaired IL-2 induced proliferation in the SHP-1 knockdown NK cells. More interestingly, these "de-regulated" SHP-1 knockdown NK cells mediated specific self-killing in a real-time live cell microscopic imaging system we developed to study NK cell cytotoxicity in vitro. Selective target recognition of the SHP-1 knockdown NK cells revealed also possible involvement of the SHP-1 phosphatase in regulating other NK functions in mature NK cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Sentman CL, Barber MA, Barber A, Zhang T (2006) NK cell receptors as tools in cancer immunotherapy. Adv Cancer Res 95: 249–292. - PubMed
-
- Lanier LL (1998) NK cell receptors. Annu Rev Immunol 16: 359–393. - PubMed
-
- Moretta L, Bottino C, Cantoni C, Mingari MC, Moretta A (2001) Human natural killer cell function and receptors. Curr Opin Pharmacol 1: 387–391. - PubMed
-
- Yokoyama WM, Plougastel BF (2003) Immune functions encoded by the natural killer gene complex. Nat Rev Immunol 3: 304–316. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

