A yeast metabolite extraction protocol optimised for time-series analyses
- PMID: 22952947
- PMCID: PMC3430680
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044283
A yeast metabolite extraction protocol optimised for time-series analyses
Abstract
There is an increasing call for the absolute quantification of time-resolved metabolite data. However, a number of technical issues exist, such as metabolites being modified/degraded either chemically or enzymatically during the extraction process. Additionally, capillary electrophoresis mass spectrometry (CE-MS) is incompatible with high salt concentrations often used in extraction protocols. In microbial systems, metabolite yield is influenced by the extraction protocol used and the cell disruption rate. Here we present a method that rapidly quenches metabolism using dry-ice ethanol bath and methanol N-ethylmaleimide solution (thus stabilising thiols), disrupts cells efficiently using bead-beating and avoids artefacts created by live-cell pelleting. Rapid sample processing minimised metabolite leaching. Cell weight, number and size distribution was used to calculate metabolites to an attomol/cell level. We apply this method to samples obtained from the respiratory oscillation that occurs when yeast are grown continuously.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
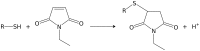
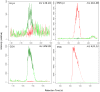
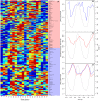
References
-
- Ban E, Park SH, Kang M-J, Lee H-J, Song EJ, et al. (2012) Growing trend of CE at the omics level: The frontier of systems biology - An update. Electrophoresis 33: 2–13. Available:http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22139583. Accessed 12 January 2012. - PubMed
-
- Buchholz A, Takors R, Wandrey C (2001) Quantification of intracellular metabolites in Escherichia coli K12 using liquid chromatographic-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometric techniques. Analytical biochemistry 295: 129–137. Available:http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11488613. Accessed 12 January 2012. - PubMed
-
- Ohta D, Kanaya S, Suzuki H (2010) Application of Fourier-transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry to metabolic profiling and metabolite identification. Current opinion in biotechnology 21: 35–44. Available:http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20171870. Accessed 12 January 2012. - PubMed
-
- Soga T, Ohashi Y, Ueno Y, Naraoka H, Tomita M, et al. (2003) Quantitative metabolome analysis using capillary electrophoresis mass spectrometry. Journal of proteome research 2: 488–494. Available:http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14582645. Accessed 3 October 2011. - PubMed
-
- Canelas AB, Ras C, Pierick A, Dam JC, Heijnen JJ, et al. (2008) Leakage-free rapid quenching technique for yeast metabolomics. Metabolomics 4: 226–239. Available:http://www.springerlink.com/content/n4w4117132644470/. Accessed 18 June 2011.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

