Expression of osteoprotegerin in placenta and its association with preeclampsia
- PMID: 22952959
- PMCID: PMC3431377
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044340
Expression of osteoprotegerin in placenta and its association with preeclampsia
Abstract
Background: Osteoprotegerin (OPG), a key regulatory factor in bone metabolism, was documented also a potential pro-angiogenic factor, which acts an important role in protecting vascular endothelial cells. Since preeclampsia has gradually been employed to be vascular diseases, we speculated that OPG might be associated with preeclampsia. The study was to evaluate the level of OPG protein and mRNA in placenta, and investigate the relationship between OPG and the pathogenesis of preeclampsia.
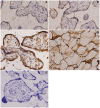
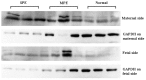
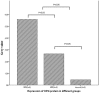
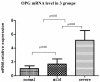
Methodology/principal findings: Placental specimens from 30 term normal pregnancy, 30 severe preeclampsia and 30 mild cases were studied. The expression and levels of OPGs' protein and mRNA were detected by immunohistochemistry, western blot analysis and real-time quantitative PCR analysis respectively. The expression of OPG protein was found in cytoplasm of placenta cytotrophoblasts and syncytiotrophoblasts in three groups. There were no significant differences of OPG protein between the maternal and fetal side in each group. The OPG protein and mRNA levels in severe preeclampsia were significantly higher than those in mild cases and normal pregnancy. However, there were no markedly differences of the OPG protein and mRNA levels between term delivery and preterm delivery in severe cases. In preeclampsia, the OPG protein and mRNA level was positively correlated with systolic blood pressure and 24 h urinary protein respectively.
Conclusions/significance: OPG protein and mRNA level in placentas of preeclampsia were found abnormal compared with normal pregnancy. In preeclampsia, the OPG protein and mRNA levels were closely related with its important clinical parameters. Taken together, OPG might be closely correlated with the pathogenesis of preeclampsia.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Yücesoy G, Ozkan S, Bodur H, Bodur H, Tan T, et al. (2005) Maternal and perinatal outcome in pregnancies complicated with hypertensive disorder of pregnancy: a seven year experience of a tertiary care center. Arch Gynecol Obstet 273(1): 43–49. - PubMed
-
- Wolf M, Sandler L, Munoz K, Hsu K, Ecker JL, et al. (2002) First trimester insulin resistance and subsequent preeclampsia: a prospective study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87(4): 1563–1568. - PubMed
-
- Brodszki J, Länne T, Laurini R, Strevens H, Wide- Swensson D, et al. (2008) Vascular mechanical properties and endothelial function in pre-eclampsia with special reference to bilateral uterine artery notch. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 87(2): 154–162. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

