Evaluation of new reference genes in papaya for accurate transcript normalization under different experimental conditions
- PMID: 22952972
- PMCID: PMC3432124
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044405
Evaluation of new reference genes in papaya for accurate transcript normalization under different experimental conditions
Abstract
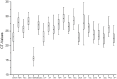
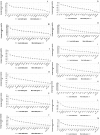
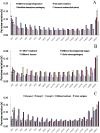
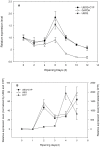
Real-time reverse transcription PCR (RT-qPCR) is a preferred method for rapid and accurate quantification of gene expression studies. Appropriate application of RT-qPCR requires accurate normalization though the use of reference genes. As no single reference gene is universally suitable for all experiments, thus reference gene(s) validation under different experimental conditions is crucial for RT-qPCR analysis. To date, only a few studies on reference genes have been done in other plants but none in papaya. In the present work, we selected 21 candidate reference genes, and evaluated their expression stability in 246 papaya fruit samples using three algorithms, geNorm, NormFinder and RefFinder. The samples consisted of 13 sets collected under different experimental conditions, including various tissues, different storage temperatures, different cultivars, developmental stages, postharvest ripening, modified atmosphere packaging, 1-methylcyclopropene (1-MCP) treatment, hot water treatment, biotic stress and hormone treatment. Our results demonstrated that expression stability varied greatly between reference genes and that different suitable reference gene(s) or combination of reference genes for normalization should be validated according to the experimental conditions. In general, the internal reference genes EIF (Eukaryotic initiation factor 4A), TBP1 (TATA binding protein 1) and TBP2 (TATA binding protein 2) genes had a good performance under most experimental conditions, whereas the most widely present used reference genes, ACTIN (Actin 2), 18S rRNA (18S ribosomal RNA) and GAPDH (Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase) were not suitable in many experimental conditions. In addition, two commonly used programs, geNorm and Normfinder, were proved sufficient for the validation. This work provides the first systematic analysis for the selection of superior reference genes for accurate transcript normalization in papaya under different experimental conditions.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Bustin SA (2002) Quantification of mRNA using real-time reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR): trends and problems. Journal of Molecular Endocrinology 29: 23. - PubMed
-
- Reece RJ (2004) Analysis of Genes and Genomes: NJ.
-
- Ginzinger DG (2002) Gene quantification using real-time quantitative PCR: An emerging technology hits the mainstream. Experimental Hematology 30: 503–512. - PubMed
-
- Huggett J, Dheda K, Bustin S, Zumla A (2005) Real-time RT-PCR normalisation; strategies and considerations. Genes Immun 6: 279–284. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

