The tonoplast-localized sucrose transporter in Populus (PtaSUT4) regulates whole-plant water relations, responses to water stress, and photosynthesis
- PMID: 22952983
- PMCID: PMC3432113
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044467
The tonoplast-localized sucrose transporter in Populus (PtaSUT4) regulates whole-plant water relations, responses to water stress, and photosynthesis
Abstract
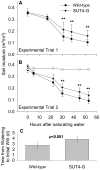
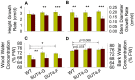
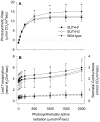
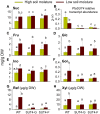
The Populus sucrose (Suc) transporter 4 (PtaSUT4), like its orthologs in other plant taxa, is tonoplast localized and thought to mediate Suc export from the vacuole into the cytosol. In source leaves of Populus, SUT4 is the predominantly expressed gene family member, with transcript levels several times higher than those of plasma membrane SUTs. A hypothesis is advanced that SUT4-mediated tonoplast sucrose fluxes contribute to the regulation of osmotic gradients between cellular compartments, with the potential to mediate both sink provisioning and drought tolerance in Populus. Here, we describe the effects of PtaSUT4-RNA interference (RNAi) on sucrose levels and raffinose family oligosaccharides (RFO) induction, photosynthesis, and water uptake, retention and loss during acute and chronic drought stresses. Under normal water-replete growing conditions, SUT4-RNAi plants had generally higher shoot water contents than wild-type plants. In response to soil drying during a short-term, acute drought, RNAi plants exhibited reduced rates of water uptake and delayed wilting relative to wild-type plants. SUT4-RNAi plants had larger leaf areas and lower photosynthesis rates than wild-type plants under well-watered, but not under chronic water-limiting conditions. Moreover, the magnitude of shoot water content, height growth, and photosynthesis responses to contrasting soil moisture regimes was greater in RNAi than wild-type plants. The concentrations of stress-responsive RFOs increased in wild-type plants but were unaffected in SUT4-RNAi plants under chronically dry conditions. We discuss a model in which the subcellular compartmentalization of sucrose mediated by PtaSUT4 is regulated in response to both sink demand and plant water status in Populus.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Penna S (2003) Building stress tolerance through over-producing trehalose in transgenic plants. Trends in Plant Science 8: 355–357. - PubMed
-
- Adams HD, Guardiola-Claramonte M, Barron-Gafford GA, Villegas JC, Breshears DD, et al. (2009) Temperature sensitivity of drought-induced tree mortality portends increased regional die-off under global-change-type drought. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 106: 7063–7066. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sala A, Piper F, Hoch G (2010) Physiological mechanisms of drought-induced tree mortality are far from being resolved. New Phytologist 186: 274–281. - PubMed
-
- Hogg EH, Brandt JP, Kochtubajda B (2002) Growth and dieback of aspen forests in northwestern Alberta, Canada, in relation to climate and insects. Canadian Journal of Forest Research 32: 823–832.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

