The protein precursors of peptides that affect the mechanics of connective tissue and/or muscle in the echinoderm Apostichopus japonicus
- PMID: 22952987
- PMCID: PMC3432112
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044492
The protein precursors of peptides that affect the mechanics of connective tissue and/or muscle in the echinoderm Apostichopus japonicus
Abstract
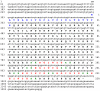
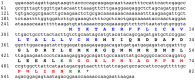
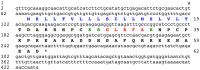
Peptides that cause muscle relaxation or contraction or that modulate electrically-induced muscle contraction have been discovered in the sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus (Phylum Echinodermata; Class Holothuroidea). By analysing transcriptome sequence data, here the protein precursors of six of these myoactive peptides (the SALMFamides Sticho-MFamide-1 and -2, NGIWYamide, stichopin, GN-19 and GLRFA) have been identified, providing novel insights on neuropeptide and endocrine-type signalling systems in echinoderms. The A. japonicus SALMFamide precursor comprises eight putative neuropeptides including both L-type and F-type SALMFamides, which contrasts with previous findings from the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus where L-type and F-type SALMFamides are encoded by different genes. The NGIWYamide precursor contains five copies of NGIWYamide but, unlike other NG peptide-type neuropeptide precursors in deuterostomian invertebrates, the NGIWYamide precursor does not have a C-terminal neurophysin domain, indicating loss of this character in holothurians. NGIWYamide was originally discovered as a muscle contractant, but it also causes stiffening of mutable connective tissue in the body wall of A. japonicus, whilst holokinins (PLGYMFR and derivative peptides) cause softening of the body wall. However, the mechanisms by which these peptides affect the stiffness of body wall connective tissue are unknown. Interestingly, analysis of the A. japonicus transcriptome reveals that the only protein containing the holokinin sequence PLGYMFR is an alpha-5 type collagen. This suggests that proteolysis of collagen may generate peptides (holokinins) that affect body wall stiffness in sea cucumbers, providing a novel perspective on mechanisms of mutable connective tissue in echinoderms.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Strand FL (1999) Neuropeptides: regulators of physiological processes. Cambridge: The MIT Press. 658 p.
-
- O'Shea M, Schaffer M (1985) Neuropeptide function: the invertebrate contribution. Annu Rev Neurosci 8: 171–198. - PubMed
-
- Greenberg MJ, Price DA (1983) Invertebrate neuropeptides: native and naturalized. Annu Rev Physiol 45: 271–288. - PubMed
-
- Lindemans M, Liu F, Janssen T, Husson SJ, Mertens I, et al. (2009) Adipokinetic hormone signaling through the gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor modulates egg-laying in Caenorhabditis elegans . Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 106: 1642–1647. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bourlat SJ, Juliusdottir T, Lowe CJ, Freeman R, Aronowicz J, et al. (2006) Deuterostome phylogeny reveals monophyletic chordates and the new phylum Xenoturbellida. Nature 444: 85–88. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

