Bilateral endoscopic medial maxillectomy for bilateral inverted papilloma
- PMID: 22953103
- PMCID: PMC3420519
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/215847
Bilateral endoscopic medial maxillectomy for bilateral inverted papilloma
Abstract
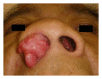
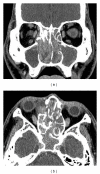
Inverted papilloma (IP) is a benign tumor of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses that is unilateral in most cases. Bilateral IP, involving both sides of the nasal cavity and sinuses, is extremely rare. This paper describes a large IP that filled in both sides of the nasal cavity and sinuses, mimicking association with malignancy. The tumor was successfully treated by bilateral endoscopic medial maxillectomy (EMM). The patient is without evidence of the disease 24 months after surgery. If preoperative diagnosis does not confirm the association with malignancy in IP, endoscopic sinus surgery (ESS) should be selected, and ESS, including EMM, is a good first choice of the treatment for IP.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endoscopic surgical treatment of nasal and paranasal sinus inverted papilloma.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1993 Dec;109(6):988-95. doi: 10.1177/019459989310900603. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1993. PMID: 8265198 Review.
-
Modification of endoscopic medial maxillectomy: a novel approach for inverted papilloma of the maxillary sinus.J Laryngol Otol. 2015 Feb;129(2):159-63. doi: 10.1017/S0022215114003144. Epub 2015 Jan 26. J Laryngol Otol. 2015. PMID: 25619402
-
Bilateral simultaneous sino-nasal inverted papilloma; A report of two cases and literature review.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2020;67:71-75. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2019.12.034. Epub 2020 Jan 9. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 32028092 Free PMC article.
-
Different endoscopic strategies in the management of recurrent sinonasal inverted papilloma.J Craniofac Surg. 2012 Jan;23(1):e44-8. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0b013e318241dae7. J Craniofac Surg. 2012. PMID: 22337461
-
[Medial maxillectomy in transitional papilloma].Acta Otorhinolaryngol Belg. 1992;46(3):273-8. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Belg. 1992. PMID: 1414309 Review. Dutch.
Cited by
-
Surgical Management of Bilateral Venous Malformation (Cavernous Hemangiomas) of the Maxillary Sinus.Case Rep Otolaryngol. 2020 Feb 10;2020:8606103. doi: 10.1155/2020/8606103. eCollection 2020. Case Rep Otolaryngol. 2020. PMID: 32095305 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hosal SA, Freeman JL. Bilateral lateral rhinotomy for resection of bilateral inverted papilloma. Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery. 1996;114(1):103–105. - PubMed
-
- Yiotakis J, Hantzakos A, Kandiloros D, Ferekidis E. A rare location of bilateral inverted papilloma of the nose and paranasal sinuses. Rhinology. 2002;40(4):220–222. - PubMed
-
- Krouse JH. Endoscopic treatment of inverted papilloma: safety and efficacy. American Journal of Otolaryngology. 2001;22(2):87–99. - PubMed
-
- Wormald PJ, Ooi E, Van Hasselt CA, Nair S. Endoscopic removal of sinonasal inverted papilloma including endoscopic medial maxillectomy. Laryngoscope. 2003;113(5):867–873. - PubMed
-
- Busquets JM, Hwang PH. Endoscopic resection of sinonasal inverted papilloma: a meta-analysis. Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery. 2006;134(3):476–482. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

