Thyroid hormone actions in liver cancer
- PMID: 22955376
- PMCID: PMC11113324
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-012-1146-7
Thyroid hormone actions in liver cancer
Abstract
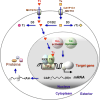
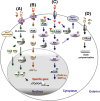
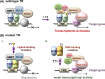
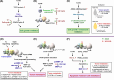
The thyroid hormone 3,3',5-triiodo-L-thyronine (T3) mediates several physiological processes, including embryonic development, cellular differentiation, metabolism, and the regulation of cell proliferation. Thyroid hormone receptors (TRs) generally act as heterodimers with the retinoid X receptor (RXR) to regulate target genes. In addition to their developmental and metabolic functions, TRs have been shown to play a tumor suppressor role, suggesting that their aberrant expression can lead to tumor transformation. Conversely, recent reports have shown an association between overexpression of wild-type TRs and tumor metastasis. Signaling crosstalk between T3/TR and other pathways or specific TR coregulators appear to affect tumor development. Since TR actions are complex as well as cell context-, tissue- and time-specific, aberrant expression of the various TR isoforms has different effects during diverse tumorigenesis. Therefore, elucidation of the T3/TR signaling mechanisms in cancers should facilitate the identification of novel therapeutic targets. This review provides a summary of recent studies focusing on the role of TRs in hepatocellular carcinomas (HCCs).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicting financial interests.
Figures


References
-
- Huang YH, Tsai MM, Lin KH. Thyroid hormone-dependent regulation of target genes and their physiological significance. Chang Gung Med J. 2008;31(4):325–334. - PubMed
-
- Pilo A, Iervasi G, Vitek F, Ferdeghini M, Cazzuola F, Bianchi R. Thyroidal and peripheral production of 3,5,3′-triiodothyronine in humans by multicompartmental analysis. Am J Physiol. 1990;258(4 Pt 1):E715–E726. - PubMed
-
- Malik R, Hodgson H. The relationship between the thyroid gland and the liver. QJM. 2002;95(9):559–569. - PubMed
-
- Dayan CM, Panicker V. Novel insights into thyroid hormones from the study of common genetic variation. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2009;5(4):211–218. - PubMed
-
- Oppenheimer JH, Schwartz HL, Surks MI. Nuclear binding capacity appears to limit the hepatic response to L-triiodothyronine (T3) Endocr Res Commun. 1975;2(4–5):309–325. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

