Application of AAPM TG 119 to volumetric arc therapy (VMAT)
- PMID: 22955639
- PMCID: PMC5718241
- DOI: 10.1120/jacmp.v13i5.3382
Application of AAPM TG 119 to volumetric arc therapy (VMAT)
Abstract
The purpose of this study was to create AAPM TG 119 benchmark plans for volumetric arc therapy (VMAT) and to compare VMAT plans with IMRT plan data. AAPM TG 119 proposes a set of test clinical cases for testing the accuracy of IMRT planning and delivery system. For these test cases, we generated two treatment plans, the first plan using 7-9 static dMLC IMRT fields and a second plan utilizing one- or two-arc VMAT technique. Dose optimization and calculations performed using 6 MV photons and Eclipse treatment planning system. Dose prescription and planning objectives were set according to the TG 119 goals. Plans were scored based on TG 119 planning objectives. Treatment plans were compared using conformity index (CI) for reference dose and homogeneity index (HI) (for D(5)-D(95)). For test cases prostate, head-and-neck, C-shape and multitarget prescription dose are 75.6 Gy, 50.4 Gy, 50 Gy and 50 Gy, respectively. VMAT dose distributions were comparable to dMLC IMRT plans. Our planning results matched TG 119 planning results. For treatment plans studied, conformity indices ranged from 1.05-1.23 (IMRT) and 1.04-1.23 (VMAT). Homogeneity indices ranged from 4.6%-11.0% (IMRT) and 4.6%-10.5% (VMAT). The ratio of total monitor units necessary for dMLC IMRT to that of VMAT was in the range of 1.1-2.0. AAPM TG 119 test cases are useful to generate VMAT benchmark plans. At preclinical implementation stage, plan comparison of VMAT and IMRT plans of AAPM TG 119 test case allowed us to understand basic capabilities of VMAT technique.
Figures

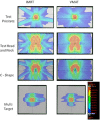


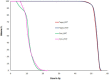

References
-
- Ling CC, Burman C, Chui CS, et al. Conformal radiation treatment of prostate cancer using inversely‐planned intensity‐modulated photon beams produced with dynamic multileaf collimation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1996;35(4):721–30. - PubMed
-
- Yu CX. Intensity‐modulated arc therapy with dynamic multileaf collimation: an alternative to tomotherapy. Phys Med Biol. 1995;40(9):1435–49. - PubMed
-
- Otto K. Volumetric modulated arc therapy: IMRT in a single gantry arc. Med Phys. 2008;35(1):310–17. - PubMed
-
- Cozzi L, Dinshaw KA, Shrivastava SK, et al. A treatment planning study comparing volumetric arc modulation with RapidArc and fixed field IMRT for cervix uteri radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol. 2008;89(2):180–91. - PubMed
-
- Clivio A, Fogliata A, Franzetti‐Pellanda A, et al. Volumetric‐modulated arc radiotherapy for carcinomas of the anal canal: a treatment planning comparison with fixed field IMRT. Radiother Oncol. 2009;92(1):118–24. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

