Microbial shifts in the swine distal gut in response to the treatment with antimicrobial growth promoter, tylosin
- PMID: 22955886
- PMCID: PMC3458334
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1205147109
Microbial shifts in the swine distal gut in response to the treatment with antimicrobial growth promoter, tylosin
Abstract
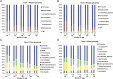
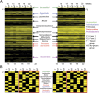
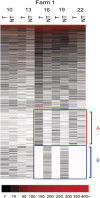
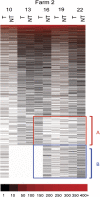
Antimicrobials have been used extensively as growth promoters (AGPs) in agricultural animal production. However, the specific mechanism of action for AGPs has not yet been determined. The work presented here was to determine and characterize the microbiome of pigs receiving one AGP, tylosin, compared with untreated pigs. We hypothesized that AGPs exerted their growth promoting effect by altering gut microbial population composition. We determined the fecal microbiome of pigs receiving tylosin compared with untreated pigs using pyrosequencing of 16S rRNA gene libraries. The data showed microbial population shifts representing both microbial succession and changes in response to the use of tylosin. Quantitative and qualitative analyses of sequences showed that tylosin caused microbial population shifts in both abundant and less abundant species. Our results established a baseline upon which mechanisms of AGPs in regulation of health and growth of animals can be investigated. Furthermore, the data will aid in the identification of alternative strategies to improve animal health and consequently production.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Jones FT, Ricke SC. Observations on the history of the development of antimicrobials and their use in poultry feeds. Poult Sci. 2003;82:613–617. - PubMed
-
- Dibner JJ, Richards JD. Antibiotic growth promoters in agriculture: History and mode of action. Poult Sci. 2005;84:634–643. - PubMed
-
- Niewold TA. The nonantibiotic anti-inflammatory effect of antimicrobial growth promoters, the real mode of action? A hypothesis. Poult Sci. 2007;86:605–609. - PubMed
-
- McEwen SA, Fedorka-Cray PJ. Antimicrobial use and resistance in animals. Clin Infect Dis. 2002;34(Suppl 3):S93–S106. - PubMed
-
- Dewey CE, Cox BD, Straw BE, Bush EJ. Use of antimicrobials in swine feeds in the United States. Swine Health and Production. 1999;7:19–25.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

