Transcription and translation are primary targets of Pim kinase inhibitor SGI-1776 in mantle cell lymphoma
- PMID: 22955922
- PMCID: PMC3482859
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2012-02-412643
Transcription and translation are primary targets of Pim kinase inhibitor SGI-1776 in mantle cell lymphoma
Abstract
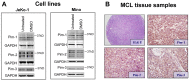
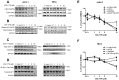
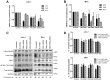
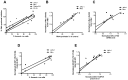
Proviral integration site for Moloney murine leukemia virus (Pim) kinases are serine/threonine/tyrosine kinases and oncoproteins that promote tumor progression. Three isoforms of Pim kinases have been identified and are known to phosphorylate numerous substrates, with regulatory functions in transcription, translation, cell cycle, and survival pathways. These kinases are involved in production, proliferation, and survival of normal B cells and are overexpressed in B-cell malignancies such as mantle cell lymphoma (MCL). SGI-1776 is a small molecule and Pim kinase inhibitor with selectivity for Pim-1. We hypothesize that Pim kinase function can be inhibited by SGI-1776 in MCL and that inhibition of phosphorylation of downstream substrates will disrupt transcriptional, translational, and cell cycle processes and promote cell death. SGI-1776 treatment in 4 MCL cell lines resulted in apoptosis induction. Phosphorylation of transcription (c-Myc) and translation targets (4E-BP1), tested in Jeko-1 and Mino, was declined. Consistent with these data, Mcl-1 and cyclin D1 protein levels were decreased. Importantly, similar to cell line data, MCL primary cells but not normal cells showed similar inhibition of substrate phosphorylation and cytotoxicity from SGI-1776 treatment. Genetic knockdown of Pim-1/Pim-2 affected similar proteins in MCL cell lines. Collectively these data demonstrate Pim kinases as therapeutic targets in MCL.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Mechanisms of cytotoxicity to Pim kinase inhibitor, SGI-1776, in acute myeloid leukemia.Blood. 2011 Jul 21;118(3):693-702. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-12-323022. Epub 2011 May 31. Blood. 2011. PMID: 21628411 Free PMC article.
-
Pim kinase inhibitor, SGI-1776, induces apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells.Blood. 2009 Nov 5;114(19):4150-7. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-03-212852. Epub 2009 Sep 4. Blood. 2009. PMID: 19734450 Free PMC article.
-
Biological effects of the Pim kinase inhibitor, SGI-1776, in multiple myeloma.Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2013 Sep;13 Suppl 2(0 2):S317-29. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2013.05.019. Epub 2013 Aug 27. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2013. PMID: 23988451 Free PMC article.
-
[The Pim family of protein kinases: structure, functions and roles in hematopoietic malignancies].Mol Biol (Mosk). 2011 Sep-Oct;45(5):755-64. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2011. PMID: 22393773 Review. Russian.
-
The Pim kinases: new targets for drug development.Curr Drug Targets. 2011 Dec;12(14):2059-66. doi: 10.2174/138945011798829447. Curr Drug Targets. 2011. PMID: 21777193 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting STAT5 or STAT5-Regulated Pathways Suppresses Leukemogenesis of Ph+ Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia.Cancer Res. 2018 Oct 15;78(20):5793-5807. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-0195. Epub 2018 Aug 28. Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30154155 Free PMC article.
-
PIM-1 kinase inhibitor SMI-4a exerts antitumor effects in chronic myeloid leukemia cells by enhancing the activity of glycogen synthase kinase 3β.Mol Med Rep. 2017 Oct;16(4):4603-4612. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7215. Epub 2017 Aug 10. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 28849186 Free PMC article.
-
Protein profiling identifies mTOR pathway modulation and cytostatic effects of Pim kinase inhibitor, AZD1208, in acute myeloid leukemia.Leuk Lymphoma. 2016 Dec;57(12):2863-2873. doi: 10.3109/10428194.2016.1166489. Epub 2016 Apr 7. Leuk Lymphoma. 2016. PMID: 27054578 Free PMC article.
-
AZD1208, a Pan-Pim Kinase Inhibitor, Has Anti-Growth Effect on 93T449 Human Liposarcoma Cells via Control of the Expression and Phosphorylation of Pim-3, mTOR, 4EBP-1, S6, STAT-3 and AMPK.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jan 16;20(2):363. doi: 10.3390/ijms20020363. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30654529 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of Pim kinase inhibitor SGI-1776 and bendamustine in B-cell lymphoma.Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2013 Sep;13 Suppl 2(0 2):S355-62. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2013.05.024. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2013. PMID: 24290221 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Romaguera JE, Fayad L, Rodriguez MA, et al. High rate of durable remissions after treatment of newly diagnosed aggressive mantle-cell lymphoma with rituximab plus hyper-CVAD alternating with rituximab plus high-dose methotrexate and cytarabine. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23(28):7013–7023. - PubMed
-
- Geisler CH, Kolstad A, Laurell A, et al. Long-term progression-free survival of mantle cell lymphoma after intensive front-line immunochemotherapy with in vivo-purged stem cell rescue: a nonrandomized phase 2 multicenter study by the Nordic Lymphoma Group. Blood. 2008;112(7):2687–2693. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cuypers HT, Selten G, Quint W, et al. Murine leukemia virus-induced T-cell lymphomagenesis: integration of proviruses in a distinct chromosomal region. Cell. 1984;37(1):141–150. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

