Knockouts reveal overlapping functions of M(2) and M(4) muscarinic receptors and evidence for a local glutamatergic circuit within the laterodorsal tegmental nucleus
- PMID: 22956788
- PMCID: PMC3545116
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.01120.2011
Knockouts reveal overlapping functions of M(2) and M(4) muscarinic receptors and evidence for a local glutamatergic circuit within the laterodorsal tegmental nucleus
Abstract
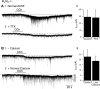
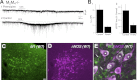
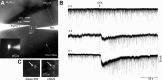
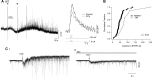
Cholinergic neurons in the laterodorsal tegmental (LDT) and peduncolopontine tegmental (PPT) nuclei regulate reward, arousal, and sensory gating via major projections to midbrain dopamine regions, the thalamus, and pontine targets. Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (mAChRs) on LDT neurons produce a membrane hyperpolarization and inhibit spike-evoked Ca(2+) transients. Pharmacological studies suggest M(2) mAChRs are involved, but the role of these and other localized mAChRs (M(1-)-M(4)) has not been definitively tested. To identify the underlying receptors and to circumvent the limited receptor selectivity of available mAChR ligands, we used light- and electron-immunomicroscopy and whole cell recording with Ca(2+) imaging in brain slices from knockout mice constitutively lacking either M(2), M(4), or both mAChRs. Immunomicroscopy findings support a role for M(2) mAChRs, since cholinergic and noncholinergic LDT and pedunculopontine tegmental neurons contain M(2)-specific immunoreactivity. However, whole cell recording revealed that the presence of either M(2) or M(4) mAChRs was sufficient, and that the presence of at least one of these receptors was required for these carbachol actions. Moreover, in the absence of M(2) and M(4) mAChRs, carbachol elicited both direct excitation and barrages of spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic potentials (sEPSPs) in cholinergic LDT neurons mediated by M(1) and/or M(3) mAChRs. Focal carbachol application to surgically reduced slices suggest that local glutamatergic neurons are a source of these sEPSPs. Finally, neither direct nor indirect excitation were knockout artifacts, since each was detected in wild-type slices, although sEPSP barrages were delayed, suggesting M(2) and M(4) receptors normally delay excitation of glutamatergic inputs. Collectively, our findings indicate that multiple mAChRs coordinate cholinergic outflow from the LDT in an unexpectedly complex manner. An intriguing possibility is that a local circuit transforms LDT muscarinic inputs from a negative feedback signal for transient inputs into positive feedback for persistent inputs to facilitate different firing patterns across behavioral states.
Figures


Similar articles
-
M1 and M4 receptors modulate hippocampal pyramidal neurons.J Neurophysiol. 2011 Feb;105(2):779-92. doi: 10.1152/jn.00686.2010. Epub 2010 Dec 15. J Neurophysiol. 2011. PMID: 21160001 Free PMC article.
-
The cholinergic agonist carbachol increases the frequency of spontaneous GABAergic synaptic currents in dorsal raphe serotonergic neurons in the mouse.Neuroscience. 2014 Jan 31;258:62-73. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.11.005. Epub 2013 Nov 11. Neuroscience. 2014. PMID: 24231737 Free PMC article.
-
Different pharmacology of N-desmethylclozapine at human and rat M2 and M 4 mAChRs in neocortex.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2015 May;388(5):487-96. doi: 10.1007/s00210-014-1080-3. Epub 2015 Jan 16. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25592256
-
Roles of the M4 acetylcholine receptor in the basal ganglia and the treatment of movement disorders.Mov Disord. 2019 Aug;34(8):1089-1099. doi: 10.1002/mds.27740. Epub 2019 Jun 18. Mov Disord. 2019. PMID: 31211471 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of neuroplasticity in cholinergic neurons of the laterodorsal tegmental nucleus for cocaine addiction.Nihon Arukoru Yakubutsu Igakkai Zasshi. 2016 Oct;51(5):259-67. Nihon Arukoru Yakubutsu Igakkai Zasshi. 2016. PMID: 30478016 Review. English, Japanese.
Cited by
-
Targeting muscarinic receptors to treat schizophrenia.Behav Brain Res. 2021 May 7;405:113201. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2021.113201. Epub 2021 Feb 26. Behav Brain Res. 2021. PMID: 33647377 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Examining the role of muscarinic M5 receptors in VTA cholinergic modulation of depressive-like and anxiety-related behaviors in rats.Neuropharmacology. 2020 Jul;171:108089. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.108089. Epub 2020 Apr 5. Neuropharmacology. 2020. PMID: 32268153 Free PMC article.
-
Electron microscopic localization of M2-muscarinic receptors in cholinergic and noncholinergic neurons of the laterodorsal tegmental and pedunculopontine nuclei of the rat mesopontine tegmentum.J Comp Neurol. 2016 Oct 15;524(15):3084-103. doi: 10.1002/cne.24010. Epub 2016 Apr 21. J Comp Neurol. 2016. PMID: 27038330 Free PMC article.
-
Off the beaten path: drug addiction and the pontine laterodorsal tegmentum.ISRN Neurosci. 2013 Jun 23;2013:604847. doi: 10.1155/2013/604847. eCollection 2013. ISRN Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24959564 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Physiological roles of CNS muscarinic receptors gained from knockout mice.Neuropharmacology. 2018 Jul 1;136(Pt C):411-420. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.09.011. Epub 2017 Sep 11. Neuropharmacology. 2018. PMID: 28911965 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baghdoyan HA. Location and quantification of muscarinic receptor subtypes in rat pons: implications for REM sleep generation. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 273: R896–R904, 1997 - PubMed
-
- Baghdoyan HA, Lydic R, Fleegal MA. M2 muscarinic autoreceptors modulate acetylcholine release in the medial pontine reticular formation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 286: 1446–1452, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Beninato M, Spencer RF. The cholinergic innervation of the rat substantia nigra: a light and electron microscopic immunohistochemical study. Exp Brain Res 72: 178–184, 1988 - PubMed
-
- Blaha CD, Allen LF, Das S, Inglis DW, Latimer MP, Vincent SR, Winn P. Modulation of dopamine efflux in the nucleus accumbens after cholinergic stimulation of the ventral tegmental area in intact, pedunculopontine nucleus-lesioned, and laterodorsal tegmental nucleus-lesioned rats. J Neurol 16: 714–722, 1996 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

