Antiphospholipase A2 receptor antibody titer and subclass in idiopathic membranous nephropathy
- PMID: 22956816
- PMCID: PMC3458465
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2012030242
Antiphospholipase A2 receptor antibody titer and subclass in idiopathic membranous nephropathy
Abstract
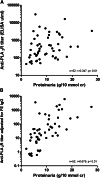
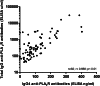
The phospholipase A(2) receptor (PLA(2)R) is the major target antigen in idiopathic membranous nephropathy. The technique for measuring antibodies against PLA(2)R and the relationship between antibody titer and clinical characteristics are not well established. Here, we measured anti-PLA(2)R (aPLA(2)R) antibody titer and subclass in a well defined cohort of 117 Caucasian patients with idiopathic membranous nephropathy and nephrotic-range proteinuria using both indirect immunofluorescence testing (IIFT) and ELISA. We assessed agreement between tests and correlated antibody titer with clinical baseline parameters and outcome. In this cohort, aPLA(2)R antibodies were positive in 74% and 72% of patients using IIFT and ELISA, respectively. Concordance between both tests was excellent (94% agreement, κ=0.85). Among 82 aPLA(2)R-positive patients, antibody titer significantly correlated with baseline proteinuria (P=0.02). Spontaneous remissions occurred significantly less frequently among patients with high antibody titers (38% versus 4% in the lowest and highest tertiles, respectively; P<0.01). IgG4 was the dominant subclass in the majority of patients. Titers of IgG4, but not IgG1 or IgG3, significantly correlated with the occurrence of spontaneous remission (P=0.03). In summary, these data show high agreement between IIFT and ELISA assessments of aPLA(2)R antibody titer and highlight the pathogenetic role of these antibodies, especially the IgG4 subclass, given the observed relationships between aPLA(2)R titer, baseline proteinuria, and outcome.
Figures

References
-
- Cattran DC: Management of membranous nephropathy: When and what for treatment. J Am Soc Nephrol 16: 1188–1194, 2005 - PubMed
-
- du Buf-Vereijken PW, Branten AJ, Wetzels JF: Idiopathic membranous nephropathy: Outline and rationale of a treatment strategy. Am J Kidney Dis 46: 1012–1029, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Glassock RJ: Secondary membranous glomerulonephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 7[Suppl 1]: 64–71, 1992 - PubMed
-
- Stanescu HC, Arcos-Burgos M, Medlar A, Bockenhauer D, Kottgen A, Dragomirescu L, Voinescu C, Patel N, Pearce K, Hubank M, Stephens HA, Laundy V, Padmanabhan S, Zawadzka A, Hofstra JM, Coenen MJ, den Heijer M, Kiemeney LA, Bacq-Daian D, Stengel B, Powis SH, Brenchley P, Feehally J, Rees AJ, Debiec H, Wetzels JF, Ronco P, Mathieson PW, Kleta R: Risk HLA-DQA1 and PLA(2)R1 alleles in idiopathic membranous nephropathy. N Engl J Med 364: 616–626, 2011 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

