Key electrophysiological, molecular, and metabolic signatures of sleep and wakefulness revealed in primary cortical cultures
- PMID: 22956841
- PMCID: PMC6621272
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2306-12.2012
Key electrophysiological, molecular, and metabolic signatures of sleep and wakefulness revealed in primary cortical cultures
Abstract
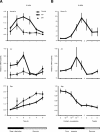
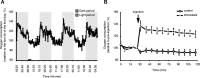
Although sleep is defined as a behavioral state, at the cortical level sleep has local and use-dependent features suggesting that it is a property of neuronal assemblies requiring sleep in function of the activation experienced during prior wakefulness. Here we show that mature cortical cultured neurons display a default state characterized by synchronized burst-pause firing activity reminiscent of sleep. This default sleep-like state can be changed to transient tonic firing reminiscent of wakefulness when cultures are stimulated with a mixture of waking neurotransmitters and spontaneously returns to sleep-like state. In addition to electrophysiological similarities, the transcriptome of stimulated cultures strikingly resembles the cortical transcriptome of sleep-deprived mice, and plastic changes as reflected by AMPA receptors phosphorylation are also similar. We used our in vitro model and sleep-deprived animals to map the metabolic pathways activated by waking. Only a few metabolic pathways were identified, including glycolysis, aminoacid, and lipids. Unexpectedly large increases in lysolipids were found both in vivo after sleep deprivation and in vitro after stimulation, strongly suggesting that sleep might play a major role in reestablishing the neuronal membrane homeostasis. With our in vitro model, the cellular and molecular consequences of sleep and wakefulness can now be investigated in a dish.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Achermann P, Borbély AA. Low-frequency (<1 Hz) oscillations in the human sleep electroencephalogram. Neuroscience. 1997;81:213–222. - PubMed
-
- Benington JH, Heller HC. Restoration of brain energy metabolism as the function of sleep. Prog Neurobiol. 1995;45:347–360. - PubMed
-
- Bersagliere A, Achermann P. Slow oscillations in human non-rapid eye movement sleep electroencephalogram: effects of increased sleep pressure. J Sleep Res. 2010;19:228–237. - PubMed
-
- Brown AM. Brain glycogen re-awakened. J Neurochem. 2004;89:537–552. - PubMed
-
- Campbell SS, Tobler I. Animal sleep: a review of sleep duration across phylogeny. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 1984;8:269–300. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
