The Longibrachiatum Clade of Trichoderma: a revision with new species
- PMID: 22956918
- PMCID: PMC3432902
- DOI: 10.1007/s13225-012-0152-2
The Longibrachiatum Clade of Trichoderma: a revision with new species
Abstract
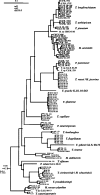
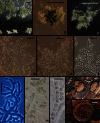
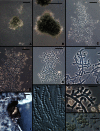
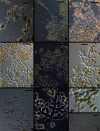
The Longibrachiatum Clade of Trichoderma is revised. Eight new species are described (T. aethiopicum, T. capillare, T. flagellatum, T. gillesii, T. gracile, T. pinnatum, T. saturnisporopsis, T. solani). The twenty-one species known to belong to the Longibrachiatum Clade are included in a synoptic key. Trichoderma parareesei and T. effusum are redescribed based on new collections or additional observations. Hypocrea teleomorphs are reported for T. gillesii and T. pinnatum. Previously described species are annotated.
Figures












References
-
- Bisby GR. Trichoderma viride Pers. ex Fries, and notes on Hypocrea. Trans Br Mycol Soc. 1939;23:149–168. doi: 10.1016/S0007-1536(39)80020-1. - DOI
-
- Bissett J. A revision of the genus Trichoderma. I. Section Longibrachiatum sect. nov. Can J Bot. 1984;62:924–931. doi: 10.1139/b84-131. - DOI
-
- Bissett J. A revision of the genus Trichoderma. II. Infrageneric classification. Can J Bot. 1991;69:2357–2372. doi: 10.1139/b91-297. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
