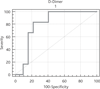
Relationship between disease severity and D-dimer levels measured with two different methods in pulmonary embolism patients
- PMID: 22958319
- PMCID: PMC3463048
- DOI: 10.1186/2049-6958-5-3-168
Relationship between disease severity and D-dimer levels measured with two different methods in pulmonary embolism patients
Abstract
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is diagnosed with increasing frequency nowadays due to advances in the diagnostic methods and the increased awareness of the disease. There is a tendency to use non invasive diagnostic methods for all diseases. D-dimer is a fibrin degradation product. We aimed to detect the relationship between disease severity and the D-dimer levels measured with two different methods. We compared D-dimer levels in cases of massive vs. non-massive PE. A total of 89 patients who were diagnosed between 2006 and 2008 were included in the study. Group 1 included patients whose D-dimer levels were measured with the immunoturbidimetric polyclonal antibody method (D-dimerPLUS®), while Group 2 patients made use of the immunoturbidimetric monoclonal antibody method (InnovanceD-DIMER®). In each group, the D-dimer levels of those with massive and non-massive PE were compared, using the Mann Whitney U test. The mean age of Group 1 (25 F/26 M) was 56.0 ± 17.9 years, and that of Group 2 (22 F/16 M) was 52.9 ± 17.9 years. There was no statistical difference in gender and mean age between the two groups (p > 0.05). In Group 1, the mean D-dimer level of massive cases (n = 7) was 1444.9 ± 657.9 μg/L and that of nonmassive PE (n = 34) was 1304.7 ± 350.5 μg/L (p > 0.05). In Group 2, the mean D-dimer level of massive cases (n = 6) was 9.7 ± 2.2 mg/L and that of non-massive PE (n = 32) was 5.9 ± 1.3 mg/L (p < 0.05). The mean D-dimer levels of massive cases as measured with the immunoturbidimetric monoclonal antibody method were significantly higher. Pulmonary embolism patients whose D-dimer levels are higher (especially higher than 6.6 mg/L) should be considered as possibly having massive embolism. Diagnostic procedures and management can be planned according to this finding.
Figures
Similar articles
-
D-dimer for risk stratification in haemodynamically stable patients with acute pulmonary embolism.Adv Med Sci. 2015 Sep;60(2):204-10. doi: 10.1016/j.advms.2015.02.005. Epub 2015 Mar 9. Adv Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 25847178
-
Investigation of relationship between the D-dimer and ischemia-modified albumin levels with the radiological imaging-based pulmonary embolism severity score in acute pulmonary embolism.Anadolu Kardiyol Derg. 2010 Aug;10(4):346-52. doi: 10.5152/akd.2010.094. Anadolu Kardiyol Derg. 2010. PMID: 20693131
-
[Pulmonary embolism in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbations of unknown origin: clinical characteristics and risk factors].Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2012 Apr;35(4):259-63. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 22781197 Chinese.
-
Exclusion of pulmonary embolism using quantitative plasma D-dimer assays.Clin Lab. 2001;47(7-8):321-6. Clin Lab. 2001. PMID: 11499792 Review.
-
A critical appraisal of non-invasive diagnosis and exclusion of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism in outpatients with suspected deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism: how many tests do we need?Int Angiol. 2005 Mar;24(1):27-39. Int Angiol. 2005. PMID: 15876996 Review.
Cited by
-
High plasma D-dimer level is associated with decreased survival in patients with lung cancer: a meta-analysis.Tumour Biol. 2013 Dec;34(6):3701-4. doi: 10.1007/s13277-013-0953-2. Epub 2013 Jul 20. Tumour Biol. 2013. PMID: 23873105
-
CT pulmonary angiography appropriateness in a single emergency department: does the use of revised Geneva score matter?Radiol Med. 2021 Dec;126(12):1544-1552. doi: 10.1007/s11547-021-01416-x. Epub 2021 Sep 13. Radiol Med. 2021. PMID: 34518985 Free PMC article.
-
[Prevalence and severity of pulmonary embolism are dependent on clinical and paraclinical parameters : Analysis of 1,943 consecutive patients with CT pulmonary angiography].Med Klin Intensivmed Notfmed. 2017 Apr;112(3):227-238. doi: 10.1007/s00063-016-0144-1. Epub 2016 Mar 1. Med Klin Intensivmed Notfmed. 2017. PMID: 26931133 German.
-
Plasma levels of D-dimer and fibrin degradation products correlate with bullous pemphigoid severity: a cross-sectional study.Sci Rep. 2021 Sep 7;11(1):17746. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-97202-w. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34493780 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma D-dimer level in early and late-onset neonatal sepsis.World J Crit Care Med. 2022 May 9;11(3):139-148. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v11.i3.139. eCollection 2022 May 9. World J Crit Care Med. 2022. PMID: 36331988 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stein PD, Hull RD, Patel KC, Olson RE, Ghali WA, Brant R, Biel RK, Bharadia V, Kalra NK. D-dimer for the exclusion of acute venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism: a systematic review. Ann Intern Med. 2004;140:589–602. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources