Role of the podocyte (and glomerular endothelium) in building the GBM
- PMID: 22958488
- PMCID: PMC3438517
- DOI: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2012.06.005
Role of the podocyte (and glomerular endothelium) in building the GBM
Abstract
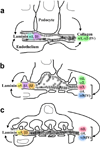
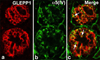
This article summarizes the basic cellular and extracellular events in the development of the glomerulus and assembly of the glomerular basement membrane (GBM), paying special attention to laminin (LM) and type IV collagen. Cellular receptors for GBM proteins, including the integrins, dystroglycan, and discoidin domain receptor 1 also are discussed. Evidence is reviewed showing that the laminin isoform present in the earliest GBM, LM-111, and final isoform found in the mature GBM, LM-521, are each derived from both endothelial cells and podocytes. Although the early collagen α1α2α1(IV) similarly derives from endothelial cells and podocytes, collagen α3α4α5(IV) found in fully mature GBM is a product solely of podocytes. Genetic diseases affecting laminin and type IV collagen synthesis also are presented, with an emphasis on mutations to LAMB2 (Pierson syndrome) and COL4A3, COL4A4, and COL4A5 (Alport syndrome), and their experimental mouse models. Stress is placed on the assembly of a compositionally correct GBM for the acquisition and maintenance of glomerular barrier properties.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Aumailley M, Bruckner-Tuderman L, Carter WG, Deutzmann R, Edgar D, Ekblom P, et al. A simplified laminin nomenclature. Matrix Biol. 2005;24:326–332. - PubMed
-
- Cheng YS, Champilaud RE, Burgeson MP, Yurchenco PD. Self-assemby of laminin isoforms. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:31525–31532. - PubMed
-
- Hudson BG. The molecular basis of Goodpasture and Alport syndromes: Beacons for the discovery of the collagen IV family. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004;15:2514–2527. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

