Regulatory T cells in induced sputum of asthmatic children: association with inflammatory cytokines
- PMID: 22958596
- PMCID: PMC3463039
- DOI: 10.1186/2049-6958-5-1-22
Regulatory T cells in induced sputum of asthmatic children: association with inflammatory cytokines
Abstract
Background and objective: CD4+CD25+ regulatory T (Treg) cells play an essential role in maintaining immune homeostasis. In this study, we investigated whether the induced sputum (IS) pool and the function of CD4+CD25+ Treg cells are altered in asthma pediatric patients.
Methods: Treg activity was studied in the IS of 40 asthmatic children. CD3+ cells were analyzed for the expression of FoxP3 mRNA by real time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). IS cells from asthmatics and controls were stained for Treg markers and analyzed by flow cytometry. We also studied the ability of Treg cells to differentiate monocytes toward alternatively activated macrophages (AAM), and to suppress proinflammatory cytokines.
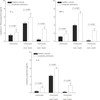
Results: (i) Mild and moderate asthmatics had significantly decreased expression of FoxP3/β-actin mRNA and decreased proportions of CD4+CD25highFoxP3+ cells compared to healthy children; (ii) patients with moderate asthma had even lower proportions of FoxP3 expression compared to mild asthmatic patients; (iii) monocytes cultured with Treg cells displayed typical features of AAM, including up-regulated expression of CD206 (macrophage mannose receptor) and CD163 (hemoglobin scavenger receptor), and an increased production of chemokine ligand 18 (CCL18). In addition, Treg cells from asthmatics have a reduced capacity to suppress LPS-proinflammatory cytokine production from monocytes/macrophages (IL-1, IL-6 and TNF-α).
Conclusion: Asthma pediatric patients display a decreased bronchial Treg population. The impaired bronchial Treg activity is associated with disease severity.
Figures



References
-
- Akdis M, Verhagen J, Taylor A, Karamloo F, Karagiannidis C, Crameri R, Thunberg S, Deniz G, Valenta R, Fiebig H, Kegel C, Disch R, Schmidt-Weber CB, Blaser K, Akdis CA. Immune responses in healthy and allergic individuals are characterized by a fine balance between allergen-specific T regulatory 1 and T helper 2 cells. J Exp Med. 2004;199:1567–1575. doi: 10.1084/jem.20032058. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

