Methotrexate-induced pneumonitis in Crohn's disease. Case report and review of the literature
- PMID: 22958737
- PMCID: PMC3463052
- DOI: 10.1186/2049-6958-5-5-312
Methotrexate-induced pneumonitis in Crohn's disease. Case report and review of the literature
Abstract
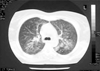
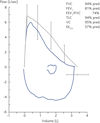
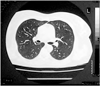
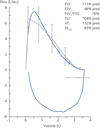
Methotrexate (MTX) is a folate-antagonist used in several neoplastic and inflammatory diseases. Reports of pulmonary complications in patients given low-dose MTX therapy are increasing. Pulmonary toxicity from MTX has a variable frequency and can present with different forms. Most often MTX-induced pneumonia in patients affected by rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is reported.In this paper we describe a case of MTX-related pneumonitis in a relatively young woman affected by Crohn's disease who presented non-productive cough, fever and dyspnea on exercise. Chest X-ray demonstrated bilateral interstitial infiltrates and at computed tomography (CT) ground-glass opacities appeared in both lungs. At spirometry an obstructive defect was demonstrated. A rapid improvement of symptoms and the regression of radiographic and spirometric alterations was achieved through MTX withdrawal and the introduction of corticosteroid therapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Drug-induced pneumonitis: the role of methotrexate.Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2001 Oct;18(3):243-52. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2001. PMID: 11587095 Review.
-
Methotrexate pneumonia lacking dyspnea and radiographic interstitial patterns during treatment for early rheumatoid arthritis: bronchoalveolar lavage and transbronchial lung biopsy in a differential diagnosis.Mod Rheumatol. 2007;17(3):256-61. doi: 10.1007/s10165-007-0578-7. Epub 2007 Jun 20. Mod Rheumatol. 2007. PMID: 17564786
-
Late-onset methotrexate-induced pneumonitis with neutrophilia in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid.BMJ Case Rep. 2014 Sep 29;2014:bcr2014206123. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2014-206123. BMJ Case Rep. 2014. PMID: 25267808 Free PMC article.
-
Successful reintroduction of methotrexate after acute pneumonitis in a patient with acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Ann Hematol. 2003 Mar;82(3):193-6. doi: 10.1007/s00277-002-0589-6. Epub 2003 Feb 15. Ann Hematol. 2003. PMID: 12634957
-
[Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia associated with low dose methotrexate treatment for malignant rheumatoid arthritis].Ryumachi. 1995 Aug;35(4):699-704. Ryumachi. 1995. PMID: 7482069 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Methotrexate-related response on human peripheral blood mononuclear cells may be modulated by the Ala16Val-SOD2 gene polymorphism.PLoS One. 2014 Oct 20;9(10):e107299. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0107299. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25330300 Free PMC article.
-
The potential role of pumpkin seeds oil on methotrexate-induced lung toxicity.Sci Rep. 2023 May 5;13(1):7321. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-34143-6. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37147356 Free PMC article.
-
Methotrexate pneumonitis in a patient with Crohn's disease, during the COVID pandemic: An unusual clinical case and review of the literature.Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 Apr;44(4):302-303. doi: 10.1016/j.gastrohep.2020.07.003. Epub 2020 Sep 16. Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 33051049 Free PMC article. Review. English, Spanish. No abstract available.
-
Methotrexate for the treatment of thyroid eye disease.J Ophthalmol. 2014;2014:128903. doi: 10.1155/2014/128903. Epub 2014 Jan 8. J Ophthalmol. 2014. PMID: 24678411 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the Cautions and Contraindications of Immunomodulator and Biologic Therapies for Use in Inflammatory Bowel Disease.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2017 Aug;23(8):1301-1315. doi: 10.1097/MIB.0000000000001199. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2017. PMID: 28708806 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ford RM. Transient pulmonary eosinophilia and asthma. A review of 20 cases occurring in 5,702 asthma sufferers. Am Rev Resp Dis. 1966;93:797–803. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

