Biosynthesis of anti-HCV compounds using thermophilic microorganisms
- PMID: 22959520
- PMCID: PMC7125738
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2012.08.045
Biosynthesis of anti-HCV compounds using thermophilic microorganisms
Abstract
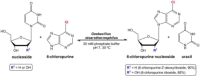
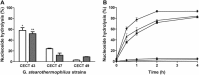
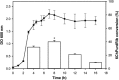
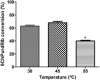
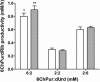
This work describes the application of thermophilic microorganisms for obtaining 6-halogenated purine nucleosides. Biosynthesis of 6-chloropurine-2'-deoxyriboside and 6-chloropurine riboside was achieved by Geobacillus stearothermophilus CECT 43 with a conversion of 90% and 68%, respectively. Furthermore, the selected microorganism was satisfactorily stabilized by immobilization in an agarose matrix. This biocatalyst can be reused at least 70 times without significant loss of activity, obtaining 379mg/L of 6-chloropurine-2'-deoxyriboside. The obtained compounds can be used as antiviral agents.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Ikejiri M., Ohshima T., Kato K., Toyama M., Murata T., Shimotohno K., Maruyama T. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. (Oxf). 2007:439. - PubMed
-
- Pankiewicz K.W., Goldstein B.M. In: Society A.C., editor. Vol. 839. American Chemical Society; Washington, DC: 2003. p. 1. (ACS Symposium Series).
-
- Trelles J.A., Valino A.L., Runza V., Lewkowicz E.S., Iribarren A.M. Biotechnol. Lett. 2005;27:759. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

