Cytokine-induced cytokine production by conventional and innate lymphoid cells
- PMID: 22959641
- PMCID: PMC4799496
- DOI: 10.1016/j.it.2012.07.006
Cytokine-induced cytokine production by conventional and innate lymphoid cells
Abstract
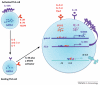
Innate immune and differentiated T cells produce signature cytokines in response to cytokine stimulation. Optimal production requires stimulation by an NF-κB inducer, most commonly an interleukin (IL)-1 family member, and a STAT activator. Usually, there is linkage between the IL-1 family member, the activated STAT and the cytokines produced: IFNγ producers respond to the IL-1 family member, IL-18 and IL-12, a STAT4 activator; IL-13 producers respond to IL-33 (although for ILC2 cells this may be replaced by IL-25) and STAT5 activators; for cells producing IL-17A or IL-22, the combination is IL-1 and a STAT3 inducer. Cytokine-induced cytokine production may have broad significance in orchestrating innate responses to distinct infectious agents and in maintaining inflammatory responses after elimination of the inciting antigen.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Janeway CA, Medzhitov R. Innate immune recognition. Ann. Rev. Immunol. 2002;20:197–216. - PubMed
-
- Takeda K, et al. Toll-like receptors. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2003;21:335–376. - PubMed
-
- Tschopp J, et al. Intracellular pattern recognition receptors in the host response. Nature. 2006;442:39–44. - PubMed
-
- Sallusto F, et al. Central memory and effector memory T cell subsets: function, generation, and maintenance. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2004;22:745–763. - PubMed
-
- Sallusto F, et al. Two subsets of memory T lymphocytes with distinct homing potentials and effector functions. Nature. 1999;401:708–712. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

