1,3-Bis(3,5-dichlorophenyl) urea compound 'COH-SR4' inhibits proliferation and activates apoptosis in melanoma
- PMID: 22959823
- PMCID: PMC3747778
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2012.08.020
1,3-Bis(3,5-dichlorophenyl) urea compound 'COH-SR4' inhibits proliferation and activates apoptosis in melanoma
Abstract
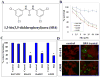
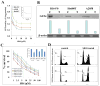
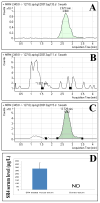
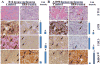
The current clinical interventions in malignant melanomas are met with poor response to therapy due to dynamic regulation of multiple melanoma signaling pathways consequent to administration of single target agents. In this context of limited response to single target agents, novel candidate molecules capable of effectively inducing tumor inhibition along with targeting multiple critical nodes of melanoma signaling assume translational significance. In this regard, we investigated the anti-cancer effects of a novel dichlorophenyl urea compound called COH-SR4 in melanoma. The SR4 treatment decreased the survival and inhibited the clonogenic potential of melanomas along with inducing apoptosis in vitro cultures. SR4 treatments lead to inhibition of GST activity along with causing G2/M phase cell cycle arrest. Oral administration of 4 mg/kg SR4 leads to effective inhibition of tumor burdens in both syngeneic and nude mouse models of melanoma. The SR4 treatment was well tolerated and no overt toxicity was observed. The histopathological examination of resected tumor sections revealed decreased blood vessels, decrease in the levels of angiogenesis marker, CD31, and proliferation marker, Ki67, along with an increase in pAMPK levels. Western blot analyses of resected tumor lysates revealed increased PARP cleavage, Bim, pAMPK along with decreased pAkt, vimentin, fibronectin, CDK4 and cyclin B1. Thus, SR4 represents a novel candidate for the further development of mono and combinatorial therapies to effectively target aggressive and therapeutically refractory melanomas.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Novel compound 1,3-bis (3,5-dichlorophenyl) urea inhibits lung cancer progression.Biochem Pharmacol. 2013 Dec 15;86(12):1664-72. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2013.09.022. Epub 2013 Oct 4. Biochem Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24099794 Free PMC article.
-
Small‑molecule COH-SR4 inhibits adipocyte differentiation via AMPK activation.Int J Mol Med. 2013 May;31(5):1166-76. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2013.1313. Epub 2013 Mar 21. Int J Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 23525347
-
Novel dichlorophenyl urea compounds inhibit proliferation of human leukemia HL-60 cells by inducing cell cycle arrest, differentiation and apoptosis.Invest New Drugs. 2012 Aug;30(4):1413-25. doi: 10.1007/s10637-011-9711-8. Epub 2011 Jul 5. Invest New Drugs. 2012. PMID: 21728022
-
Fisetin, a phytochemical, potentiates sorafenib-induced apoptosis and abrogates tumor growth in athymic nude mice implanted with BRAF-mutated melanoma cells.Oncotarget. 2015 Sep 29;6(29):28296-311. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5064. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26299806 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro and in vivo anti-tumor activity of CoQ0 against melanoma cells: inhibition of metastasis and induction of cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis through modulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways.Oncotarget. 2016 Apr 19;7(16):22409-26. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7983. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26968952 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Noncoupled Mitochondrial Respiration as Therapeutic Approach for the Treatment of Metabolic Diseases: Focus on Transgenic Animal Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 18;24(22):16491. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216491. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38003681 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioenergetic modulation with the mitochondria uncouplers SR4 and niclosamide prevents proliferation and growth of treatment-naïve and vemurafenib-resistant melanomas.Oncotarget. 2018 Dec 11;9(97):36945-36965. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.26421. eCollection 2018 Dec 11. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 30651927 Free PMC article.
-
Novel compound 1,3-bis (3,5-dichlorophenyl) urea inhibits lung cancer progression.Biochem Pharmacol. 2013 Dec 15;86(12):1664-72. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2013.09.022. Epub 2013 Oct 4. Biochem Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24099794 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial Uncoupling: A Key Controller of Biological Processes in Physiology and Diseases.Cells. 2019 Jul 30;8(8):795. doi: 10.3390/cells8080795. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31366145 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Topical 2'-Hydroxyflavanone for Cutaneous Melanoma.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Oct 14;11(10):1556. doi: 10.3390/cancers11101556. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31615091 Free PMC article.
References
-
- MacKie RM. Incidence, risk factors and prevention of melanoma. Eur J Cancer. 1998;34:S3–6. - PubMed
-
- Albert VA, Koh HK, Geller AC, Miller DR, Prout MN, Lew RA. Years of potential life lost: Another indicator of the impact of cutaneous malignant melanoma on society. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1990;23:308–10. - PubMed
-
- Lea CS, Scotto JA, Buffler PA, Fine J, Barnhill RL, Berwick M. Ambient UVB and melanoma risk in the United States: A case-control analysis. Ann Epidemiol. 2007;17:447–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

