Effects of ethanol, Δ(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol, or their combination on object recognition memory and object preference in adolescent and adult male rats
- PMID: 22959891
- PMCID: PMC3477605
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neulet.2012.08.037
Effects of ethanol, Δ(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol, or their combination on object recognition memory and object preference in adolescent and adult male rats
Abstract
Recent advances have been made in our understanding of the deleterious effects of both ethanol and THC on adolescent behavior and brain development. However, very little is known about the combined effects of EtOH+THC during adolescence, a time in which these drugs are often used together. The purpose of this experiment was to: (1) determine whether EtOH and/or THC induced greater working memory impairment in adolescent than adult male rats using the novel object recognition (NOR) task and (2) determine whether the EtOH+THC combination would produce a more potent additive effect in adolescents than adults when compared to these drugs alone. NOR was performed with a 24h delay under each of the four drug conditions: vehicle; 1.5g/kg ethanol; 1.0mg/kg THC; and 1.5g/kg EtOH+1.0mg/kg THC, at 72h intervals. The results show that there was an age effect on working memory in NOR after the EtOH+THC challenge. Specifically, adolescent animals showed a preference for the familiar object whereas adults showed no preference for the novel or familiar object, the latter being characteristic of a classic working memory deficit. These effects were not dependent on changes in exploration across session, global activity across drug condition, or total object exploration. These novel findings clearly indicate that further understanding of this age-drug interaction is crucial to elucidating the influence that adolescent EtOH+THC use may have on repeated drug use and abuse later in life.
Published by Elsevier Ireland Ltd.
Figures
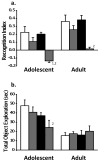
 Ethanol; ■ THC;
Ethanol; ■ THC;
 Ethanol + THC) on novel object recognition performance were significant, p = 0.006, and p ≤ 0.001, respectively. (Panel a) Recognition index: (Novel − Familiar)/(Novel + Familiar) +/− SEM. (Panel b) Total object inspection time: (Novel + Familiar) +/− SEM. 1 p<0.05 compared to zero; 2 p<0.05 compared to vehicle.
Ethanol + THC) on novel object recognition performance were significant, p = 0.006, and p ≤ 0.001, respectively. (Panel a) Recognition index: (Novel − Familiar)/(Novel + Familiar) +/− SEM. (Panel b) Total object inspection time: (Novel + Familiar) +/− SEM. 1 p<0.05 compared to zero; 2 p<0.05 compared to vehicle.References
-
- Monti PM, et al. Adolescence: booze, brains, and behavior. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2005;29(2):207–20. - PubMed
-
- White AM, Swartzwelder HS. Age-related effects of alcohol on memory and memory-related brain function in adolescents and adults. Recent Dev Alcohol. 2005;17:161–76. - PubMed
-
- Cha YM, et al. Sex differences in the effects of delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol on spatial learning in adolescent and adult rats. Behav Pharmacol. 2007;18(5–6):563–9. - PubMed
-
- Cha YM, et al. Differential effects of delta9-THC on learning in adolescent and adult rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2006;83(3):448–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

