Automated processing integrated with a microflow cytometer for pathogen detection in clinical matrices
- PMID: 22960010
- PMCID: PMC5012219
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bios.2012.08.015
Automated processing integrated with a microflow cytometer for pathogen detection in clinical matrices
Abstract
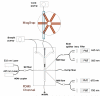
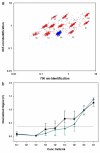
A spinning magnetic trap (MagTrap) for automated sample processing was integrated with a microflow cytometer capable of simultaneously detecting multiple targets to provide an automated sample-to-answer diagnosis in 40 min. After target capture on fluorescently coded magnetic microspheres, the magnetic trap automatically concentrated the fluorescently coded microspheres, separated the captured target from the sample matrix, and exposed the bound target sequentially to biotinylated tracer molecules and streptavidin-labeled phycoerythrin. The concentrated microspheres were then hydrodynamically focused in a microflow cytometer capable of 4-color analysis (two wavelengths for microsphere identification, one for light scatter to discriminate single microspheres and one for phycoerythrin bound to the target). A three-fold decrease in sample preparation time and an improved detection limit, independent of target preconcentration, was demonstrated for detection of Escherichia coli 0157:H7 using the MagTrap as compared to manual processing. Simultaneous analysis of positive and negative controls, along with the assay reagents specific for the target, was used to obtain dose-response curves, demonstrating the potential for quantification of pathogen load in buffer and serum.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Catch and release: integrated system for multiplexed detection of bacteria.Anal Chem. 2013 May 21;85(10):4944-50. doi: 10.1021/ac303801v. Epub 2013 Apr 30. Anal Chem. 2013. PMID: 23631439 Free PMC article.
-
A sensitive biosensor using double-layer capillary based immunomagnetic separation and invertase-nanocluster based signal amplification for rapid detection of foodborne pathogen.Biosens Bioelectron. 2018 Feb 15;100:583-590. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2017.10.005. Epub 2017 Oct 3. Biosens Bioelectron. 2018. PMID: 29032045
-
Detection of E. coli O157:H7 by immunomagnetic separation coupled with fluorescence immunoassay.Biosens Bioelectron. 2011 Dec 15;30(1):337-41. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2011.09.029. Epub 2011 Oct 1. Biosens Bioelectron. 2011. PMID: 22005594
-
Multi-wavelength microflow cytometer using groove-generated sheath flow.Lab Chip. 2009 Jul 7;9(13):1942-50. doi: 10.1039/b822442k. Epub 2009 Mar 31. Lab Chip. 2009. PMID: 19532970 Free PMC article.
-
Immunosensors for rapid detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 - perspectives for use in the meat processing industry.Food Microbiol. 2008 Feb;25(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2007.07.005. Epub 2007 Jul 31. Food Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 17993371 Review.
Cited by
-
Suspension arrays based on nanoparticle-encoded microspheres for high-throughput multiplexed detection.Chem Soc Rev. 2015 Aug 7;44(15):5552-95. doi: 10.1039/c4cs00382a. Epub 2015 May 29. Chem Soc Rev. 2015. PMID: 26021602 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The intersection of flow cytometry with microfluidics and microfabrication.Lab Chip. 2014 Mar 21;14(6):1044-59. doi: 10.1039/c3lc51152a. Lab Chip. 2014. PMID: 24488050 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A low-cost, multiplexable, automated flow cytometry procedure for the characterization of microbial stress dynamics in bioreactors.Microb Cell Fact. 2013 Oct 31;12:100. doi: 10.1186/1475-2859-12-100. Microb Cell Fact. 2013. PMID: 24176169 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in microfluidic devices made from thermoplastics used in cell biology and analyses.Biomicrofluidics. 2017 Oct 24;11(5):051502. doi: 10.1063/1.4998604. eCollection 2017 Sep. Biomicrofluidics. 2017. PMID: 29152025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in automated real-time flow cytometry for monitoring of bioreactor processes.Eng Life Sci. 2021 Nov 12;22(3-4):260-278. doi: 10.1002/elsc.202100082. eCollection 2022 Mar. Eng Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 35382548 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dzenitis JM, Makarewicz AJ. In: The Microflow Cytometer. Kim JS, Ligler F, editors. Pan Stanford Publishing Pte Ltd; Singapore: 2010. pp. 263–286.
-
- Gervais L, de Rooij N, Delamarche E. Advanced Materials. 2011;23(24):H151–H176. - PubMed
-
- Golden JP, Kim J, Anderson GP, Hashemi N, Howell PJ, Ligler FS. A Microflow Cytometer on a Chip. SPIE. 2010;7553:755308-1–755808-6.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

