Automated processing integrated with a microflow cytometer for pathogen detection in clinical matrices
- PMID: 22960010
- PMCID: PMC5012219
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bios.2012.08.015
Automated processing integrated with a microflow cytometer for pathogen detection in clinical matrices
Abstract
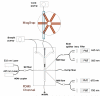
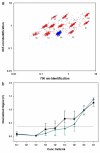
A spinning magnetic trap (MagTrap) for automated sample processing was integrated with a microflow cytometer capable of simultaneously detecting multiple targets to provide an automated sample-to-answer diagnosis in 40 min. After target capture on fluorescently coded magnetic microspheres, the magnetic trap automatically concentrated the fluorescently coded microspheres, separated the captured target from the sample matrix, and exposed the bound target sequentially to biotinylated tracer molecules and streptavidin-labeled phycoerythrin. The concentrated microspheres were then hydrodynamically focused in a microflow cytometer capable of 4-color analysis (two wavelengths for microsphere identification, one for light scatter to discriminate single microspheres and one for phycoerythrin bound to the target). A three-fold decrease in sample preparation time and an improved detection limit, independent of target preconcentration, was demonstrated for detection of Escherichia coli 0157:H7 using the MagTrap as compared to manual processing. Simultaneous analysis of positive and negative controls, along with the assay reagents specific for the target, was used to obtain dose-response curves, demonstrating the potential for quantification of pathogen load in buffer and serum.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures


References
-
- Dzenitis JM, Makarewicz AJ. In: The Microflow Cytometer. Kim JS, Ligler F, editors. Pan Stanford Publishing Pte Ltd; Singapore: 2010. pp. 263–286.
-
- Gervais L, de Rooij N, Delamarche E. Advanced Materials. 2011;23(24):H151–H176. - PubMed
-
- Golden JP, Kim J, Anderson GP, Hashemi N, Howell PJ, Ligler FS. A Microflow Cytometer on a Chip. SPIE. 2010;7553:755308-1–755808-6.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

