Structural biology of the PCI-protein fold
- PMID: 22960705
- PMCID: PMC3675071
- DOI: 10.4161/bioa.21131
Structural biology of the PCI-protein fold
Abstract
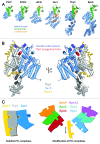
The PCI fold is based on a stack of α-helices topped with a winged-helix domain and is found in a range of proteins that form central parts of large complexes such as the proteasome lid, the COP9 signalosome, elongation factor eIF3, and the TREX-2 complex. Recent structural determinations have given intriguing insight into how these folds function both to facilitate the generation of larger proteinaceous assembles and also to interact functionally with nucleic acids.
Keywords: COP9 complex; PCI fold; PCI protein; TREX-2 complex; eIF3; proteasome.
Figures
References
-
- García-Oliver E, García-Molinero V, Rodríguez-Navarro S. mRNA export and gene expression: The SAGA-TREX-2 connection. Biochim Biophys Acta. 20121819:555–65. - PubMed
-
- Valkov E., Dean JC, Jani D, Kuhlmann SI, Stewart M. Structural basis for the assembly and disassembly of mRNA nuclear export complexes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 20121819:578–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
