Autologous intravenous bone marrow mononuclear cell therapy for patients with subacute ischaemic stroke: a pilot study
- PMID: 22960888
- PMCID: PMC3461733
Autologous intravenous bone marrow mononuclear cell therapy for patients with subacute ischaemic stroke: a pilot study
Abstract
Background & objectives: Bone marrow mononuclear cell therapy has emerged as one of the option for the treatment of Stroke. Several preclinical studies have shown that the treatment with mononuclear cell (MNCs) can reduce the infarct size and improve the functional outcome. We evaluated the feasibility, safety and clinical outcome of administering bone marrow mononuclear cell (MNCs) intravenously to patients with subacute ischaemic stroke.
Methods: In a non-randomized phase-I clinical study, 11 consecutive, eligible and consenting patients, aged 30-70 yr with ischaemic stroke involving anterior circulation within 7 to 30 days of onset of stroke were included. Bone marrow was aspirated from iliac crest and the harvested mononuclear cells were infused into antecubital vein. Outcomes measured for safety included immediate reactions after cell infusion and evidence of tumour formation at one year in whole body PET scan. Patients were followed at week 1, 4-6, 24 and 52 to determine clinical progress using National Institute of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS), Barthel Index (BI), modified Rankin Scale (mRS), MRI, EEG and PET. Feasibility outcomes included target-dose feasibility. Favourable clinical outcome was defined as mRS score of 2 or less or BI score of 75 to 100 at six months after stem cell therapy.
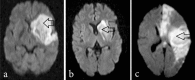
Results: Between September 2006 and April 2007, 11 patients were infused with bone-marrow mononuclear cells (mean 80 million with CD-34 + mean 0.92 million). Protocol was target-dose feasible in 9 patients (82%). FDG-PET scan at 24 and 52 wk in nine patients did not reveal evidence of tumour formation. Seven patients had favourable clinical outcome.
Interpretation & conclusions: Intravenous bone marrow mononuclear cell therapy appears feasible and safe in patients with subacute ischaemic stroke. Further, a randomized controlled trial to examine its efficacy is being conducted.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01501773.
Figures

References
-
- Sarti C, Rastenyte D, Cepaitis Z, Tuomilehto J. International trends in mortality from stroke, 1968 to 1994. Stroke. 2000;31:1588–601. - PubMed
-
- Adams HP, Jr, del Zoppo G, Alberts MJ, Bhatt DL, Brass L, Furlan A, et al. Guidelines for the early management of adults with ischemic stroke: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association Stroke Council, Clinical Cardiology Council, Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention Council, and the Atherosclerotic Peripheral Vascular Disease and Quality of Care Outcomes in Research Interdisciplinary Working Groups. Stroke. 2007;38:1655–711. - PubMed
-
- Kamiya N, Ueda M, Igarashi H, Nishiyama Y, Suda S, Inaba T, et al. Intra-arterial transplantation of bone marrow mononuclear cells immediately after reperfusion decreases brain injury after focal ischemia in rats. Life Sci. 2008;83:433–7. - PubMed
-
- Giraldi-Guimarães A, Rezende-Lima M, Bruno FP, Mendez-Otero R. Treatment with bone marrow mononuclear cells induces functional recovery and decreases neurodegeneration after sensorimotor cortical ischemia in rats. Brain Res. 2009;1256:108–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
