A multiply redundant genetic switch 'locks in' the transcriptional signature of regulatory T cells
- PMID: 22961053
- PMCID: PMC3698954
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.2420
A multiply redundant genetic switch 'locks in' the transcriptional signature of regulatory T cells
Abstract
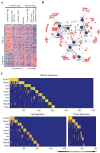
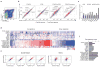
The transcription factor Foxp3 participates dominantly in the specification and function of Foxp3(+)CD4(+) regulatory T cells (T(reg) cells) but is neither strictly necessary nor sufficient to determine the characteristic T(reg) cell signature. Here we used computational network inference and experimental testing to assess the contribution of other transcription factors to this. Enforced expression of Helios or Xbp1 elicited distinct signatures, but Eos, IRF4, Satb1, Lef1 and GATA-1 elicited exactly the same outcome, acting in synergy with Foxp3 to activate expression of most of the T(reg) cell signature, including key transcription factors, and enhancing occupancy by Foxp3 at its genomic targets. Conversely, the T(reg) cell signature was robust after inactivation of any single cofactor. A redundant genetic switch thus 'locked in' the T(reg) cell phenotype, a model that would account for several aspects of T(reg) cell physiology, differentiation and stability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures




Comment in
-
The Foxp3 interactome: a network perspective of T(reg) cells.Nat Immunol. 2012 Oct;13(10):943-5. doi: 10.1038/ni.2424. Nat Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22990900 No abstract available.
References
-
- Sakaguchi S, Yamaguchi T, Nomura T, Ono M. Regulatory T cells and immune tolerance. Cell. 2008;133:775–787. - PubMed
-
- Curotto de Lafaille MA, Lafaille JJ. Natural and adaptive foxp3+ regulatory T cells: more of the same or a division of labor? Immunity. 2009;30:626–635. - PubMed
-
- Duarte JH, et al. Natural Treg cells spontaneously differentiate into pathogenic helper cells in lymphopenic conditions. Eur J Immunol. 2009;39:948–955. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

