Differential gene expression pattern in early gastric cancer by an integrative systematic approach
- PMID: 22961301
- PMCID: PMC3982715
- DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2012.1621
Differential gene expression pattern in early gastric cancer by an integrative systematic approach
Abstract
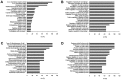
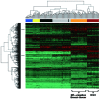
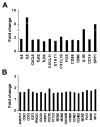
To elucidate the molecular basis of early gastric cancer (EGC), the genome-wide expression pattern of cancer and normal tissues from 27 patients were analyzed by a microarray-based method. Using an integrative systematic bioinformatics approach, we classified the differentially expressed genes in EGC. Interestingly, the more highly expressed genes in EGC exhibited the most significant correlation with cell migration and metastasis. This implies that, even at the early stage of gastric cancer, the molecular properties usually observed in late-stage cancer are already present. Furthermore, we have found a novel association between the expression pattern and molecular pathways of EGC and estrogen receptor α (ERα)-negative breast cancer through cross-experimental analysis. These results provide new insights into the biological properties of EGC, as well as yielding useful basic data for the study of molecular mechanisms of EGC carcinogenesis.
Figures


References
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108. - PubMed
-
- Vecchi M, Nuciforo P, Romagnoli S, et al. Gene expression analysis of early and advanced gastric cancers. Oncogene. 2007;26:4284–4294. - PubMed
-
- Nam SY, Choi IJ, Park KW, et al. Effect of repeated endoscopic screening on the incidence and treatment of gastric cancer in health screenees. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;21:855–860. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

