Neurological perspectives on voltage-gated sodium channels
- PMID: 22961543
- PMCID: PMC3437034
- DOI: 10.1093/brain/aws225
Neurological perspectives on voltage-gated sodium channels
Abstract
The activity of voltage-gated sodium channels has long been linked to disorders of neuronal excitability such as epilepsy and chronic pain. Recent genetic studies have now expanded the role of sodium channels in health and disease, to include autism, migraine, multiple sclerosis, cancer as well as muscle and immune system disorders. Transgenic mouse models have proved useful in understanding the physiological role of individual sodium channels, and there has been significant progress in the development of subtype selective inhibitors of sodium channels. This review will outline the functions and roles of specific sodium channels in electrical signalling and disease, focusing on neurological aspects. We also discuss recent advances in the development of selective sodium channel inhibitors.
Figures
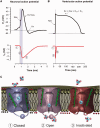
References
-
- Abrahamsen B, Zhao J, Asante CO, Cendan CM, Marsh S, Martinez-Barbera JP, et al. The cell and molecular basis of mechanical, cold, and inflammatory pain. Science. 2008;321:702–5. - PubMed
-
- Ahmad S, Dahllund L, Eriksson AB, Hellgren D, Karlsson U, Lund PE, et al. A stop codon mutation in SCN9A causes lack of pain sensation. Hum Mol Genet. 2007;16:2114–21. - PubMed
-
- Akopian AN, Sivilotti L, Wood JN. A tetrodotoxin-resistant voltage-gated sodium channel expressed by sensory neurons. Nature. 1996;379:257–62. - PubMed
-
- Akopian AN, Souslova V, England S, Okuse K, Ogata N, Ure J, et al. The tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium channel SNS has a specialized function in pain pathways. Nat Neurosci. 1999;2:541–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

