Proteomic profiling identifies dysregulated pathways in small cell lung cancer and novel therapeutic targets including PARP1
- PMID: 22961666
- PMCID: PMC3567922
- DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0112
Proteomic profiling identifies dysregulated pathways in small cell lung cancer and novel therapeutic targets including PARP1
Abstract
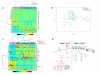
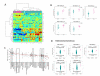
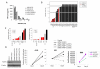
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive malignancy distinct from non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in its metastatic potential and treatment response. Using an integrative proteomic and transcriptomic analysis, we investigated molecular differences contributing to the distinct clinical behavior of SCLCs and NSCLCs. SCLCs showed lower levels of several receptor tyrosine kinases and decreased activation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) and Ras/mitogen-activated protein (MAP)/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) kinase (MEK) pathways but significantly increased levels of E2F1-regulated factors including enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2), thymidylate synthase, apoptosis mediators, and DNA repair proteins. In addition, PARP1, a DNA repair protein and E2F1 co-activator, was highly expressed at the mRNA and protein levels in SCLCs. SCLC growth was inhibited by PARP1 and EZH2 knockdown. Furthermore, SCLC was significantly more sensitive to PARP inhibitors than were NSCLCs, and PARP inhibition downregulated key components of the DNA repair machinery and enhanced the efficacy of chemotherapy.
Significance: SCLC is a highly lethal cancer with a 5-year survival rate of less than 10%. To date, no molecularly targeted agents have prolonged survival in patients with SCLCs. As a step toward identifying new targets, we systematically profiled SCLCs with a focus on therapeutically relevant signaling pathways. Our data reveal fundamental differences in the patterns of pathway activation in SCLCs and NSCLCs and identify several potential therapeutic targets for SCLCs, including PARP1 and EZH2. On the basis of these results, clinical studies evaluating PARP and EZH2 inhibition, together with chemotherapy or other agents, warrant further investigation.
Figures


Comment in
-
A genetic snapshot of small cell lung cancer.Cancer Discov. 2012 Sep;2(9):769-71. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0346. Cancer Discov. 2012. PMID: 22969115
References
-
- Govindan R, Page N, Morgensztern D, Read W, Tierney R, Vlahiotis A, et al. Changing epidemiology of small-cell lung cancer in the United States over the last 30 years: analysis of the surveillance, epidemiologic, and end results database. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:4539–44. - PubMed
-
- Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2129–39. - PubMed
-
- Paez JG, Janne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S, Greulich H, Gabriel S, et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 2004;304:1497–500. - PubMed
-
- Soda M, Choi YL, Enomoto M, Takada S, Yamashita Y, Ishikawa S, et al. Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature. 2007;448:561–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

