Reactivation of ERK signaling causes resistance to EGFR kinase inhibitors
- PMID: 22961667
- PMCID: PMC3477553
- DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0103
Reactivation of ERK signaling causes resistance to EGFR kinase inhibitors
Abstract
The clinical efficacy of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) kinase inhibitors is limited by the development of drug resistance. The irreversible EGFR kinase inhibitor WZ4002 is effective against the most common mechanism of drug resistance mediated by the EGFR T790M mutation. Here, we show, in multiple complementary models, that resistance to WZ4002 develops through aberrant activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling caused by either an amplification of mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 (MAPK1) or by downregulation of negative regulators of ERK signaling. Inhibition of MAP-ERK kinase (MEK) or ERK restores sensitivity to WZ4002 and prevents the emergence of drug resistance. We further identify MAPK1 amplification in an erlotinib-resistant EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung carcinoma patient. In addition, the WZ4002-resistant MAPK1-amplified cells also show an increase both in EGFR internalization and a decrease in sensitivity to cytotoxic chemotherapy. Our findings provide insights into mechanisms of drug resistance to EGFR kinase inhibitors and highlight rational combination therapies that should be evaluated in clinical trials.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest for all authors. All authors have completed separate conflict of interest forms.
No conflicts of interest
Figures
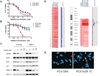

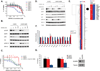



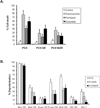
References
-
- Rosell R, Carcereny E, Gervais R, Vergnenegre A, Massuti B, Felip E, et al. Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012 - PubMed
-
- Zhou C, Wu YL, Chen G, Feng J, Liu XQ, Wang C, et al. Erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2011;12:735–742. - PubMed
-
- Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, Yang CH, Chu DT, Saijo N, et al. Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:947–957. - PubMed
-
- Engelman JA, Janne PA. Mechanisms of acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:2895–2899. - PubMed
-
- Kobayashi S, Boggon TJ, Dayaram T, Janne PA, Kocher O, Meyerson M, et al. EGFR mutation and resistance of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:786–792. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

