A differing role of oxidative stress in the regulation of central and peripheral hemodynamics during exercise in heart failure
- PMID: 22961867
- PMCID: PMC3517640
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00568.2012
A differing role of oxidative stress in the regulation of central and peripheral hemodynamics during exercise in heart failure
Abstract
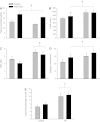
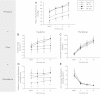
This study sought to characterize the role of free radicals in regulating central and peripheral hemodynamics at rest and during exercise in patients with heart failure (HF). We examined cardiovascular responses to dynamic handgrip exercise (4, 8, and 12 kg at 1 Hz) following consumption of either a placebo or acute oral antioxidant cocktail (AOC) consisting of vitamin C, E, and α-lipoic acid in a balanced, crossover design. Central and peripheral hemodynamics, mean arterial pressure, cardiac index, systemic vascular resistance (SVR), brachial artery blood flow, and peripheral (arm) vascular resistance (PVR) were determined in 10 HF patients and 10 age-matched controls. Blood assays evaluated markers of oxidative stress and efficacy of the AOC. When compared with controls, patients with HF exhibited greater oxidative stress, measured by malondialdehyde (+36%), and evidence of endogenous antioxidant compensation, measured by greater superoxide dismutase activity (+83%). The AOC increased plasma ascorbate (+50%) in both the HF patients and controls, but significant systemic hemodynamic effects were only evident in the patients with HF, both at rest and throughout exercise. Specifically, the AOC reduced mean arterial pressure (-5%) and SVR (-12%) and increased cardiac index (+7%) at each workload. In contrast, peripherally, brachial artery blood flow and PVR (arm) were unchanged by the AOC. In conclusion, these data imply that SVR in patients with HF is, at least in part, mediated by oxidative stress. However, this finding does not appear to be the direct result of muscle-specific changes in PVR.
Figures
References
-
- Alves M, Dos Santos MR, Nobre TS, Martinez D, Pereira Barretto AC, Brum PC, Rondon MU, Middlekauff HR, Negrao CE. Mechanisms of blunted muscle vasodilation during peripheral chemoreceptor stimulation in heart failure patients. Hypertension 60: 669–676, 2012 - PubMed
-
- Barretto AC, Santos AC, Munhoz R, Rondon MU, Franco FG, Trombetta IC, Roveda F, de Matos LN, Braga AM, Middlekauff HR, Negrao CE. Increased muscle sympathetic nerve activity predicts mortality in heart failure patients. Int J Cardiol 135: 302–307, 2009 - PubMed
-
- Bogert LW, van Lieshout JJ. Non-invasive pulsatile arterial pressure and stroke volume changes from the human finger. Exp Physiol 90: 437–446, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Bos WJ, Imholz BP, van Goudoever J, Wesseling KH, van Montfrans GA. The reliability of noninvasive continuous finger blood pressure measurement in patients with both hypertension and vascular disease. Am J Hypertens 5: 529–535, 1992 - PubMed
-
- Cohen-Solal A, Logeart D, Guiti C, Dahan M, Gourgon R. Cardiac and peripheral responses to exercise in patients with chronic heart failure. Eur Heart J 20: 931–945, 1999 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

