Identification and characterization of distinct C-terminal domains of the human hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor-2 that are essential for receptor export, constitutive activity, desensitization, and internalization
- PMID: 22962331
- PMCID: PMC3502627
- DOI: 10.1124/mol.112.081307
Identification and characterization of distinct C-terminal domains of the human hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor-2 that are essential for receptor export, constitutive activity, desensitization, and internalization
Abstract
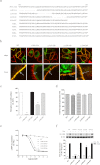
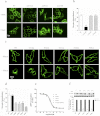
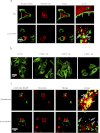
The human hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor 2 (HCA₂), also known as GPR109A and HM74a, was first identified as a niacin receptor and has recently received significant attention because of its potential to clinically modify plasma lipids in a favorable manner. Our recent studies have demonstrated that the niacin-induced internalization of HCA₂ receptors is regulated by G protein-coupled receptor kinase (GRK) 2 and arrestin3 and that internalized receptors rapidly recycle back to the cell surface. The investigation presented here used a combination of amino acid deletion and site-directed mutagenesis to identify structural and functional domains within the HCA₂ C terminus and explore their potential roles in receptor phosphorylation, desensitization, and internalization. We first constructed four mutants with deletions of 10 to 15 amino acids each that were distinct from truncated mutants. We successfully identified different domains responsible for receptor export, constitutive activity, desensitization, phosphorylation, and internalization. We also generated a comprehensive series of alanine substitution mutants, replacing conserved serine and threonine residues in the C terminus with alanine residues to pinpoint the key residues that are essential for GRK2-mediated phosphorylation and arrestin3 association. Moreover, we found that a sequence from residues 329 to 343 in the C-terminal tail of HCA₂ plays a crucial role in keeping HCA₂ in an inactive conformation. These data demonstrate the importance of distinct domains within the C terminus of HCA₂ for receptor cell surface expression, desensitization, and internalization and phosphorylation and stabilization of an inactive receptor conformation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Identification of distinct c-terminal domains of the Bombyx adipokinetic hormone receptor that are essential for receptor export, phosphorylation and internalization.Cell Signal. 2011 Sep;23(9):1455-65. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2011.04.006. Epub 2011 Apr 21. Cell Signal. 2011. PMID: 21536126
-
Internalization of the human nicotinic acid receptor GPR109A is regulated by G(i), GRK2, and arrestin3.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jul 16;285(29):22605-18. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.087213. Epub 2010 May 11. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20460384 Free PMC article.
-
Homologous desensitization of signalling by the beta (beta) isoform of the human thromboxane A2 receptor.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006 Sep;1761(9):1114-31. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2006.07.012. Epub 2006 Aug 3. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006. PMID: 16956790
-
Differential requirements of arrestin-3 and clathrin for ligand-dependent and -independent internalization of human G protein-coupled receptor 40.Cell Signal. 2014 Nov;26(11):2412-23. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.07.019. Epub 2014 Jul 16. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 25038452
-
International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. LXXXII: Nomenclature and Classification of Hydroxy-carboxylic Acid Receptors (GPR81, GPR109A, and GPR109B).Pharmacol Rev. 2011 Jun;63(2):269-90. doi: 10.1124/pr.110.003301. Epub 2011 Mar 31. Pharmacol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21454438 Review.
Cited by
-
Nicotinic acid timed to feeding reverses tissue lipid accumulation and improves glucose control in obese Zucker rats[S].J Lipid Res. 2017 Jan;58(1):31-41. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M068395. Epub 2016 Nov 15. J Lipid Res. 2017. PMID: 27875257 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic coding variants in the niacin receptor, hydroxyl-carboxylic acid receptor 2, and response to niacin therapy.Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2017 Aug;27(8):285-293. doi: 10.1097/FPC.0000000000000289. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28628560 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Rare and potentially pathogenic variants in hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor genes identified in breast cancer cases.BMC Med Genomics. 2021 Dec 1;14(1):284. doi: 10.1186/s12920-021-01126-3. BMC Med Genomics. 2021. PMID: 34852802 Free PMC article.
-
Dosing profile profoundly influences nicotinic acid's ability to improve metabolic control in rats.J Lipid Res. 2015 Sep;56(9):1679-90. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M058149. Epub 2015 Jul 13. J Lipid Res. 2015. PMID: 26168997 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bermak JC, Li M, Bullock C, Zhou QY. (2001) Regulation of transport of the dopamine D1 receptor by a new membrane-associated ER protein. Nat Cell Biol 3:492–498 - PubMed
-
- Bouvier M, Hausdorff WP, De Blasi A, O'Dowd BF, Kobilka BK, Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ. (1988) Removal of phosphorylation sites from the β2-adrenergic receptor delays onset of agonist-promoted desensitization. Nature 333:370–373 - PubMed
-
- Cerione RA, Codina J, Benovic JL, Lefkowitz RJ, Birnbaumer L, Caron MG. (1984) The mammalian β2-adrenergic receptor: reconstitution of functional interactions between pure receptor and pure stimulatory nucleotide binding protein of the adenylate cyclase system. Biochemistry 23:4519–4525 - PubMed
-
- Claeysen S, Sebben M, Becamel C, Bockaert J, Dumuis A. (1999) Novel brain-specific 5-HT4 receptor splice variants show marked constitutive activity: role of the C-terminal intracellular domain. Mol Pharmacol 55:910–920 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

