Gβγ inhibits exocytosis via interaction with critical residues on soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein-25
- PMID: 22962332
- PMCID: PMC3502621
- DOI: 10.1124/mol.112.080507
Gβγ inhibits exocytosis via interaction with critical residues on soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein-25
Abstract
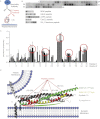
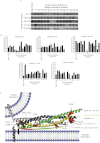
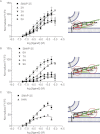
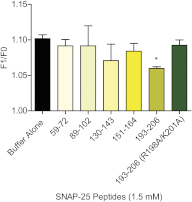
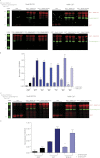
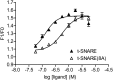
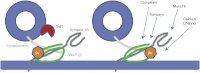
Spatial and temporal regulation of neurotransmitter release is a complex process accomplished by the exocytotic machinery working in tandem with numerous regulatory proteins. G-protein βγ dimers regulate the core process of exocytosis by interacting with the soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor (SNARE) proteins soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein-25 (SNAP-25), syntaxin 1A, and synaptobrevin. Gβγ binding to ternary SNAREs overlaps with calcium-dependent binding of synaptotagmin, inhibiting synaptotagmin-1 binding and fusion of the synaptic vesicle. To further explore the binding sites of Gβγ on SNAP-25, peptides based on the sequence of SNAP-25 were screened for Gβγ binding. Peptides that bound Gβγ were subjected to alanine scanning mutagenesis to determine their relevance to the Gβγ-SNAP-25 interaction. Peptides from this screen were tested in protein-protein interaction assays for their ability to modulate the interaction of Gβγ with SNAP-25. A peptide from the C terminus, residues 193 to 206, significantly inhibited the interaction. In addition, Ala mutants of SNAP-25 residues from the C terminus of SNAP-25, as well as from the amino-terminal region decreased binding to Gβ₁γ₁. When SNAP-25 with eight residues mutated to alanine was assembled with syntaxin 1A, there was significantly reduced affinity of this mutated t-SNARE for Gβγ, but it still interacted with synaptotagmin-1 in a Ca²⁺ -dependent manner and reconstituted evoked exocytosis in botulinum neurotoxin E-treated neurons. However, the mutant SNAP-25 could no longer support 5-hydroxytryptamine-mediated inhibition of exocytosis.
Figures

References
-
- Binz T, Blasi J, Yamasaki S, Baumeister A, Link E, Südhof TC, Jahn R, Niemann H. (1994) Proteolysis of SNAP-25 by types E and A botulinal neurotoxins. J Biol Chem 269:1617–1620 - PubMed
-
- Blackmer T, Larsen EC, Bartleson C, Kowalchyk JA, Yoon EJ, Preininger AM, Alford S, Hamm HE, Martin TF. (2005) G protein βγ directly regulates SNARE protein fusion machinery for secretory granule exocytosis. Nat Neurosci 8:421–425 - PubMed
-
- Blackmer T, Larsen EC, Takahashi M, Martin TF, Alford S, Hamm HE. (2001) G protein βγ subunit-mediated presynaptic inhibition: regulation of exocytotic fusion downstream of Ca2+ entry. Science 292:293–297 - PubMed
-
- Brose N, Petrenko AG, Südhof TC, Jahn R. (1992) Synaptotagmin—a calcium sensor on the synaptic vesicle surface. Science 256(5059):1021–1025 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

