Structure Activity Relationships for Derivatives of Adenosine-5'-Triphosphate as Agonists at P(2) Purinoceptors: Heterogeneity Within P(2X) and P(2Y) Subtypes
- PMID: 22962511
- PMCID: PMC3434461
- DOI: 10.1002/ddr.430310308
Structure Activity Relationships for Derivatives of Adenosine-5'-Triphosphate as Agonists at P(2) Purinoceptors: Heterogeneity Within P(2X) and P(2Y) Subtypes
Abstract
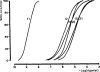
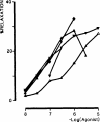
The structure-activity relationships for a variety of adenine nucleotide analogues at P(2x)- and P(2Y)-purinoceptors were investigated. Compounds formed by structural modifications of the ATP molecule including substitutions of the purine ring (C2, C8, N1, and N(6)-substituents, and a uridine base instead of adenine), the ribose moiety (2' and 3'-positions), and the triphosphate group (lower phosphates, bridging oxygen substitution, and cyclization) were prepared. Pharmacological activity at P(2Y)-purinoceptors was assayed in the guinea pig taenia coli, endothelial cells of the rabbit aorta, smooth muscle of the rabbit mesenteric artery, and turkey erythrocyte membranes. Activity at P(2X)-purinoceptors was assayed in the rabbit saphenous artery and the guinea-pig vas deferens and urinary bladder. Some of the analogues displayed selectivity, or even specificity, for either the P(2X)- or the P(2Y)-purinoceptors. Certain analogues displayed selectivity or specificity within the P(2X)- or P(2Y)-purinoceptor superfamilies, giving hints about possible subclasses. For example, 8-(6-aminohexylamino)ATP and 2',3'-isopropylidene-AMP were selective for endothelial Pzypurinoceptors over P(2Y)-purinoceptors in the guinea pig taenia coli, rabbit aorta, and turkey erythrocytes. These compounds were both inactive at P(2X)-purinoceptors. The potent agonist N(6)-methyl ATP and the somewhat less potent agonist 2'-deoxy-ATP were selective for P(2Y)-purinoceptors in the guinea pig taenia coli, but were inactive at P(2X)-purinoceptors and the vascular P(2Y)-purinoceptors. 3'-Benzylamino-3'-deoxyATP was very potent at the P(2X)-purinoceptors in the guinea pig vas deferens and bladder, but not in the rabbit saphenous artery and was inactive at P(2Y) receptors. These data suggest that specific compounds can be developed that can be utilized to activate putative subtypes of the P(2X)- and P(2Y)-purinoceptor classes.
Figures
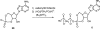



References
-
- Abbracchio MP, Cattabeni F, Fredholm BB, Williams M. Purinoceptor nomenclature: A status report. Drug Dev Res. 1993;28:207–213.
-
- Allsup DJ, Boarder MR. Comparison of P2 purinergic recepters of aortic endothelial cells with those of adrenal medulla: Evidence for heterogeneity of receptor subtype and of inositol phosphate response. Mol Pharmacol. 1991;38:84–91. - PubMed
-
- Bean BP. Pharmacology and electrophysiology of ATP-activated ion channels. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992;13:87–90. - PubMed
-
- Benham CD, Tsien RW. A novel receptor-operated Ca2+ - permeable channel activated by ATP in smooth muscle. Nature. 1987;328:275–278. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

