Video Rating in Neurodegenerative Disease Clinical Trials: The Experience of PRION-1
- PMID: 22962552
- PMCID: PMC3435531
- DOI: 10.1159/000339730
Video Rating in Neurodegenerative Disease Clinical Trials: The Experience of PRION-1
Abstract
Background/aims: Large clinical trials including patients with uncommon diseases involve assessors in different geographical locations, resulting in considerable inter-rater variability in assessment scores. As video recordings of examinations, which can be individually rated, may eliminate such variability, we measured the agreement between a single video rater and multiple examining physicians in the context of PRION-1, a clinical trial of the antimalarial drug quinacrine in human prion diseases.
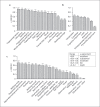
Methods: We analysed a 43-component neurocognitive assessment battery, on 101 patients with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, focusing on the correlation and agreement between examining physicians and a single video rater.
Results: In total, 335 videos of examinations of 101 patients who were video-recorded over the 4-year trial period were assessed. For neurocognitive examination, inter-observer concordance was generally excellent. Highly visual neurological examination domains (e.g. finger-nose-finger assessment of ataxia) had good inter-rater correlation, whereas those dependent on non-visual clues (e.g. power or reflexes) correlated poorly. Some non-visual neurological domains were surprisingly concordant, such as limb muscle tone.
Conclusion: Cognitive assessments and selected neurological domains can be practically and accurately recorded in a clinical trial using video rating. Video recording of examinations is a valuable addition to any trial provided appropriate selection of assessment instruments is used and rigorous training of assessors is undertaken.
Keywords: Clinical trial; Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease; PRION-1; Rating scale; Video rating.
Figures

References
-
- Doody RS, Gavrilova SI, Sano M, et al. Effect of dimebon on cognition, activities of daily living, behaviour, and global function in patients with mild-to-moderate Alzheimer's disease: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Lancet. 2008;372:207–215. - PubMed
-
- Feldman HH, Doody RS, Kivipelto M, et al. Randomized controlled trial of atorvastatin in mild to moderate Alzheimer disease: LEADe. Neurology. 2010;74:956–964. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

