Ribavirin enhances the action of interferon-α against hepatitis C virus by promoting the p53 activity through the ERK1/2 pathway
- PMID: 22962590
- PMCID: PMC3433463
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043824
Ribavirin enhances the action of interferon-α against hepatitis C virus by promoting the p53 activity through the ERK1/2 pathway
Abstract
Background/aims: Ribavirin significantly enhances the antiviral response of interferon-α (IFN-α) against Hepatitis C virus (HCV), but the underlying mechanisms remain poorly understood. Recently, p53 has been identified as an important factor involving the suppression of HCV replication in hepatocytes. We, therefore, decided to investigate whether and how ribavirin inhibits the replication of HCV by promoting the activity of p53.
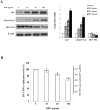
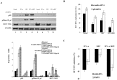
Methods: HepG2 and HCV replicons (JFH1/HepG2) were utilized to study the relationship between ribavirin and p53. The effect of ribavirin on cell cycles was analyzed by flow cytometry. The activation of p53 and the signaling pathways were determined using immunoblotting. By knocking down ERK1/ERK2 and p53 utilizing RNA interference strategy, we further assessed the role of ERK1/2 and p53 in the suppression of HCV replication by ribavirin in a HCV replicon system.
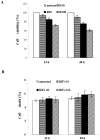
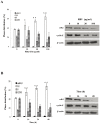
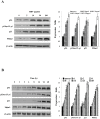
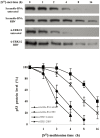
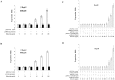
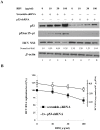
Results: Using HepG2 and HCV replicons, we demonstrated that ribavirin caused the cell cycle arrest at G1 phase and stabilized and activated p53, which was associated with the antiviral activity of ribavirin. Compared to either ribavirin or IFN-α alone, ribavirin plus IFN-α resulted in greater p53 activation and HCV suppression. We further identified ERK1/2 that linked ribavirin signals to p53 activation. More importantly, knockdown of ERK1/2 and p53 partially mitigated the inhibitory effects of ribavirin on the HCV replication, indicating that ERK1/2-p53 pathway was involved in the anti-HCV effects of ribavirin.
Conclusion: Ribavirin stimulates ERK1/2 and subsequently promotes p53 activity which at least partly contributes to the enhanced antiviral response of IFN-α plus ribavirin against HCV.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Synergistic inhibition of intracellular hepatitis C virus replication by combination of ribavirin and interferon- alpha.J Infect Dis. 2004 Apr 1;189(7):1129-39. doi: 10.1086/382595. Epub 2004 Mar 16. J Infect Dis. 2004. PMID: 15031779
-
Ribavirin up-regulates the activity of double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase and enhances the action of interferon-alpha against hepatitis C virus.J Infect Dis. 2007 Aug 1;196(3):425-34. doi: 10.1086/518894. Epub 2007 Jun 25. J Infect Dis. 2007. PMID: 17597457
-
IFN-λ Inhibits MiR-122 Transcription through a Stat3-HNF4α Inflammatory Feedback Loop in an IFN-α Resistant HCV Cell Culture System.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 11;10(12):e0141655. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0141655. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26657215 Free PMC article.
-
Life style-related diseases of the digestive system: cell culture system for the screening of anti-hepatitis C virus (HCV) reagents: suppression of HCV replication by statins and synergistic action with interferon.J Pharmacol Sci. 2007 Oct;105(2):145-50. doi: 10.1254/jphs.fm0070050. Epub 2007 Oct 6. J Pharmacol Sci. 2007. PMID: 17928739 Review.
-
The metabolism, pharmacokinetics and mechanisms of antiviral activity of ribavirin against hepatitis C virus.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2006 Apr;63(7-8):832-42. doi: 10.1007/s00018-005-5455-y. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2006. PMID: 16501888 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pegylated IFN-α suppresses hepatitis C virus by promoting the DAPK-mTOR pathway.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Dec 20;113(51):14799-14804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1618517114. Epub 2016 Dec 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27930338 Free PMC article.
-
Research Progress of Drug Treatment in Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2020 May 13;21(4):130. doi: 10.1208/s12249-020-01679-z. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2020. PMID: 32405780 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interferon and ribavirin combination treatment synergistically inhibit HCV internal ribosome entry site mediated translation at the level of polyribosome formation.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 23;8(8):e72791. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0072791. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. Retraction in: PLoS One. 2024 Aug 5;19(8):e0308579. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0308579. PMID: 24009705 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Controversies' clarification regarding ribavirin efficacy in measles and coronaviruses: Comprehensive therapeutic approach strictly tailored to COVID-19 disease stages.World J Clin Cases. 2021 Jul 6;9(19):5135-5178. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i19.5135. World J Clin Cases. 2021. PMID: 34307564 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction and Characterisation of the System Effects of Aristolochic Acid: A Novel Joint Network Analysis towards Therapeutic and Toxicological Mechanisms.Sci Rep. 2015 Dec 1;5:17646. doi: 10.1038/srep17646. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26620132 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pawlotsky JM, Dahari H, Neumann AU, Hezode C, Germanidis G, et al. (2004) Antiviral action of ribavirin in chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology 126: 703–714. - PubMed
-
- Bodenheimer HC Jr, Lindsay KL, Davis GL, Lewis JH, Thung SN, et al. (1997) Tolerance and efficacy of oral ribavirin treatment of chronic hepatitis C: A multicenter trial. Hepatology 26: 473–477. - PubMed
-
- Zhou S, Liu R, Baroudy BM, Malcolm BA, Reyes GR (2003) The effect of ribavirin and IMPDH inhibitors on hepatitis C virus subgenomic replicon RNA. Virology 310: 333–342. - PubMed
-
- Reyes GR (2001) Ribavirin: recent insights into antiviral mechanisms of action. Curr Opin Drug Dev 4: 651–656. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

