MiR-214 targets β-catenin pathway to suppress invasion, stem-like traits and recurrence of human hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 22962603
- PMCID: PMC3433464
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044206
MiR-214 targets β-catenin pathway to suppress invasion, stem-like traits and recurrence of human hepatocellular carcinoma
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2012;7(9). doi:10.1371/annotation/1be2a62e-45a1-4c13-9a8d-f265005a21e0
Abstract
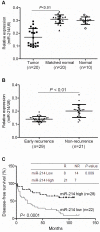
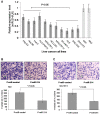
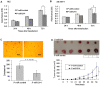
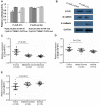
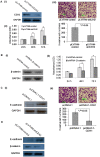
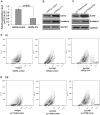
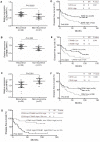
The down-regulation of miR-214 has previously been observed in human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Here, we demonstrated the down-regulation of miR-214 is associated with cell invasion, stem-like traits and early recurrence of HCC. Firstly, we validated the suppression of miR-214 in human HCC by real-time quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) in 20 paired tumor and non-tumor liver tissues of HCC patients and 10 histologically normal liver tissues from colorectal cancer patients with liver metastases. Further qRT-PCR analysis of 50 HCC tissues from an independent cohort of HCC patients of whom 29 with early recurrent disease (<2 years) and 21 with late recurrent disease demonstrated that the suppression of miR-214 was significantly more suppressed in samples from HCC patients with early recurrent disease compared those from patients with no recurrence. Re-expression of miR-214 significantly suppressed the growth of HCC cells in vitro and reduced their tumorigenicity in vivo. The enhancer of zeste homologue 2 (EZH2) and β-catenin (CTNNB1) was identified as two potential direct downstream targets of miR-214 through bioinformatics analysis and experimentally validated the miRNA-target interactions with a dual-firefly luciferase reporter assay. In corroborate with this, both EZH2 and CTNNB1 are found to be significantly overexpressed in human HCC biopsies. Since EZH2 can regulate CTNNB1, CTNNB1 can also be an indirect target of miR-214 through EZH2. Silencing EZH2 or CTNNB1 expression suppressed the growth and invasion of HCC cells and induced E-cadherin (CDH1), known to inhibit cell invasion and metastasis. Furthermore, the silencing of miR-214 or overexpression of EZH2 increased EpCAM(+) stem-like cells through the activation of CTNNB1. Interestingly, the up-regulation of EZH2, CTNNB1 and the down-regulation of CDH1 in HCC patients correlated with early recurrent disease and can be an independent predictor of poor survival. Therefore, miR-214 can directly or indirectly target CTNNB1 to modulate the β-catenin signaling pathway in HCC.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Sanyal AJ, Yoon SK, Lencioni R (2010) The Etiology of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Consequences for Treatment. The Oncologist 15: 14–22. - PubMed
-
- Jemal A, Bray F (2011) Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, et al (2011) Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 61: 69–90. - PubMed
-
- Pei Y, Zhang T, Renault V, Zhang X (2009) An overview of hepatocellular carcinoma study by omics-based methods. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 41: 1–15. - PubMed
-
- Wang SM, Ooi LLPJ, Hui KM (2011) Upregulation of Rac GTPase-Activating Protein 1 Is Significantly Associated with the Early Recurrence of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 17: 6040–6051. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

