A snapshot of histone modifications within transposable elements in Drosophila wild type strains
- PMID: 22962605
- PMCID: PMC3433462
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044253
A snapshot of histone modifications within transposable elements in Drosophila wild type strains
Abstract
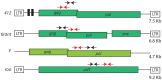
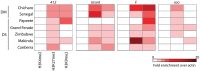
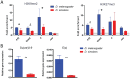
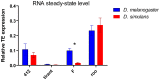
Transposable elements (TEs) are a major source of genetic variability in genomes, creating genetic novelty and driving genome evolution. Analysis of sequenced genomes has revealed considerable diversity in TE families, copy number, and localization between different, closely related species. For instance, although the twin species Drosophila melanogaster and D. simulans share the same TE families, they display different amounts of TEs. Furthermore, previous analyses of wild type derived strains of D. simulans have revealed high polymorphism regarding TE copy number within this species. Several factors may influence the diversity and abundance of TEs in a genome, including molecular mechanisms such as epigenetic factors, which could be a source of variation in TE success. In this paper, we present the first analysis of the epigenetic status of four TE families (roo, tirant, 412 and F) in seven wild type strains of D. melanogaster and D. simulans. Our data shows intra- and inter-specific variations in the histone marks that adorn TE copies. Our results demonstrate that the chromatin state of common TEs varies among TE families, between closely related species and also between wild type strains.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Biemont C, Vieira C (2006) Genetics: junk DNA as an evolutionary force. Nature 443: 521–524. - PubMed
-
- Rebollo R, Horard B, Hubert B, Vieira C (2010) Jumping genes and epigenetics: Towards new species. Gene 454: 1–7. - PubMed
-
- Muotri AR, Marchetto MC, Coufal NG, Gage FH (2007) The necessary junk: new functions for transposable elements. Hum Mol Genet 16 Spec No. 2: R159–167. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

