High-throughput sequencing and characterization of the small RNA transcriptome reveal features of novel and conserved microRNAs in Panax ginseng
- PMID: 22962612
- PMCID: PMC3433442
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044385
High-throughput sequencing and characterization of the small RNA transcriptome reveal features of novel and conserved microRNAs in Panax ginseng
Abstract
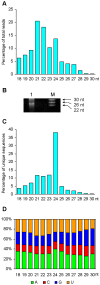
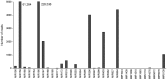
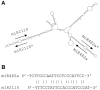
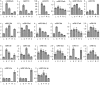
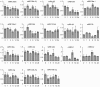
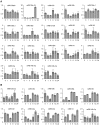
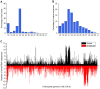
microRNAs (miRNAs) play vital regulatory roles in many organisms through direct cleavage of transcripts, translational repression, or chromatin modification. Identification of miRNAs has been carried out in various plant species. However, no information is available for miRNAs from Panax ginseng, an economically significant medicinal plant species. Using the next generation high-throughput sequencing technology, we obtained 13,326,328 small RNA reads from the roots, stems, leaves and flowers of P. ginseng. Analysis of these small RNAs revealed the existence of a large, diverse and highly complicated small RNA population in P. ginseng. We identified 73 conserved miRNAs, which could be grouped into 33 families, and 28 non-conserved ones belonging to 9 families. Characterization of P. ginseng miRNA precursors revealed many features, such as production of two miRNAs from distinct regions of a precursor, clusters of two precursors in a transcript, and generation of miRNAs from both sense and antisense transcripts. It suggests the complexity of miRNA production in P. ginseng. Using a computational approach, we predicted for the conserved and non-conserved miRNA families 99 and 31 target genes, respectively, of which eight were experimentally validated. Among all predicted targets, only about 20% are conserved among various plant species, whereas the others appear to be non-conserved, indicating the diversity of miRNA functions. Consistently, many miRNAs exhibited tissue-specific expression patterns. Moreover, we identified five dehydration- and ten heat-responsive miRNAs and found the existence of a crosstalk among some of the stress-responsive miRNAs. Our results provide the first clue to the elucidation of miRNA functions in P. ginseng.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Dey L, Xie JT, Wang A, Wu J, Maleckar SA, et al. (2003) Anti-hyperglycemic effects of ginseng: comparison between root and berry. Phytomedicine 10: 600–605. - PubMed
-
- Larsen MW, Moser C, Hoiby N, Song Z, Kharazmi A (2004) Ginseng modulates the immune response by induction of interleukin-12 production. APMIS 112: 369–373. - PubMed
-
- Lee MH, Jeong JH, Seo JW, Shin CG, Kim YS, et al. (2004) Enhanced triterpene and phytosterol biosynthesis in Panax ginseng overexpressing squalene synthase gene. Plant Cell Physiol 45: 976–984. - PubMed
-
- O’Hara M, Kiefer D, Farrell K, Kemper K (1998) A review of 12 commonly used medicinal herbs. Arch Fam Med 7: 523–536. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

