In vivo screening for secreted proteins that modulate glucose handling identifies interleukin-6 family members as potent hypoglycemic agents
- PMID: 22962620
- PMCID: PMC3433445
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044600
In vivo screening for secreted proteins that modulate glucose handling identifies interleukin-6 family members as potent hypoglycemic agents
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2012;7(11). doi:10.1371/annotation/6e392eb7-55cb-4bc6-ab8e-bd8130ad6582. Carolan, Peter C [corrected to Carolan, Peter J]
Abstract
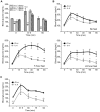
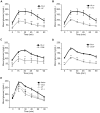
Diabetes is a disease of abnormal glucose homeostasis characterized by chronic hyperglycemia and a broad array of consequent organ damage. Because normal glucose homeostasis is maintained by a complex interaction between behavior (feeding and physical activity) and metabolic activity that is modulated by inter-organ signaling through secreted factors, disease modeling in vitro is necessarily limited. In contrast, in vivo studies allow complex metabolic phenotypes to be studied but present a barrier to high throughput studies. Here we present the development of a novel in vivo screening platform that addresses this primary limitation of in vivo experimentation. Our platform leverages the large secretory capacity of the liver and the hepatocyte transfection technique of hydrodynamic tail vein injection to achieve supraphysiologic blood levels of secreted proteins. To date, the utility of hydrodynamic transfection has been limited by the deleterious impact of the variable transfection efficiency inherent to this technique. We overcome this constraint by co-transfection of a secreted luciferase cDNA whose product can be easily monitored in the blood of a living animal and used as a surrogate marker for transfection efficiency and gene expression levels. To demonstrate the utility of our strategy, we screened 248 secreted proteins for the ability to enhance glucose tolerance. Surprisingly, interleukin-6 and several of its family members but not other well-recognized insulin sensitizing agents were identified as potent hypoglycemic factors. We propose this experimental system as a powerful and flexible in vivo screening platform for identifying genes that modulate complex behavioral and metabolic phenotypes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
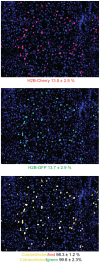
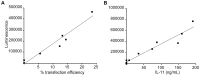
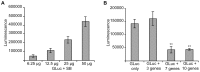
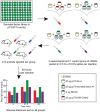
References
-
- Danaei G, Finucane MM, Lu Y, Singh GM, Cowan MJ, et al. (2011) National, regional, and global trends in fasting plasma glucose and diabetes prevalence since 1980: systematic analysis of health examination surveys and epidemiological studies with 370 country-years and 2.7 million participants. Lancet 378: 31–40. - PubMed
-
- Seidell JC (2000) Obesity, insulin resistance and diabetes–a worldwide epidemic. Br J Nutr 83 Suppl 1: S5–8. - PubMed
-
- Curioni CC, Lourenco PM (2005) Long-term weight loss after diet and exercise: a systematic review. Int J Obes (Lond) 29: 1168–1174. - PubMed
-
- Tong PC, Ko GT, So WY, Chiang SC, Yang X, et al. (2008) Use of anti-diabetic drugs and glycaemic control in type 2 diabetes-tThe Hong Kong Diabetes Registry. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 82: 346–352. - PubMed
-
- Wing RR, Venditti E, Jakicic JM, Polley BA, Lang W (1998) Lifestyle intervention in overweight individuals with a family history of diabetes. Diabetes Care 21: 350–359. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

