Telocytes in the urinary system
- PMID: 22963412
- PMCID: PMC3527325
- DOI: 10.1186/1479-5876-10-188
Telocytes in the urinary system
Abstract
Background: Telocytes, a new type of interstitial cells, have been identified in many organs in mammals. The present studies aimed at investigating the ultrastructure, distribution and interactions of telocytes with surrounding cells in the urinary system of rats, to confirm the existence of telocytes in kidneys, ureter and urinary bladder.
Methods: Samples of kidney, ureter, or urinary bladder were harvested for the ultrastructure by the electron microscope. The primary culture of telocytes was performed to investigate the dynamic alterations.
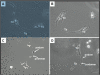
Results: Telocytes mainly located in the sub-capsular space of kidney, or between smooth muscle bundles and in the lamina propria of ureter and urinary bladder. Telocytes established numerous contacts with macrophages in the sub-capsular space of kidney, or with smooth muscle cells, nerve endings as well as blood capillaries in the ureter and urinary bladder. The complete morphology of telocytes with telopodes was observed clearly through the primary cell culture from the kidney tissues of rats.
Conclusions: Our data evidenced the existence of telocytes in the urinary system, which may contribute to the tissue reparation and regeneration.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

