Regulation of Toll-like receptor 2 interaction with Ecgp96 controls Escherichia coli K1 invasion of brain endothelial cells
- PMID: 22963587
- PMCID: PMC3524395
- DOI: 10.1111/cmi.12026
Regulation of Toll-like receptor 2 interaction with Ecgp96 controls Escherichia coli K1 invasion of brain endothelial cells
Abstract
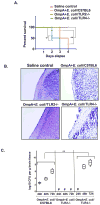
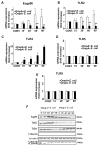
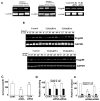
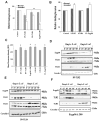
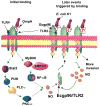
The interaction of outer membrane protein A (OmpA) with its receptor, Ecgp96 (a homologue of Hsp90β), is critical for the pathogenesis of Escherichia coli K1 meningitis. Since Hsp90 chaperones Toll-like receptors (TLRs), we examined the role of TLRs in E. coli K1 infection. Herein, we show that newborn TLR2(-/-) mice are resistant to E. coli K1 meningitis, while TLR4(-/-) mice succumb to infection sooner. In vitro, OmpA+ E. coli infection selectively upregulates Ecgp96 and TLR2 in human brain microvascular endothelial cells (HBMEC), whereas OmpA- E. coli upregulates TLR4 in these cells. Furthermore, infection with OmpA+ E. coli causes Ecgp96 and TLR2 translocate to the plasma membrane of HBMEC as a complex. Immunoprecipitation studies of the plasma membrane fractions from infected HBMEC reveal that the C termini of Ecgp96 and TLR2 are critical for OmpA+ E. coli invasion. Knockdown of TLR2 using siRNA results in inefficient membrane translocation of Ecgp96 and significantly reduces invasion. In addition, the interaction of Ecgp96 andTLR2 induces a bipartite signal, one from Ecgp96 through PKC-α while the other from TLR2 through MyD88, ERK1/2 and NF-κB. This bipartite signal ultimately culminates in the efficient production of NO, which in turn promotes E. coli K1 invasion of HBMEC.
© 2012 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Identification of minimum carbohydrate moiety in N-glycosylation sites of brain endothelial cell glycoprotein 96 for interaction with Escherichia coli K1 outer membrane protein A.Microbes Infect. 2014 Jul;16(7):540-52. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2014.06.002. Epub 2014 Jun 13. Microbes Infect. 2014. PMID: 24932957 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental validation of the predicted binding site of Escherichia coli K1 outer membrane protein A to human brain microvascular endothelial cells: identification of critical mutations that prevent E. coli meningitis.J Biol Chem. 2010 Nov 26;285(48):37753-61. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.122804. Epub 2010 Sep 17. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20851887 Free PMC article.
-
IQGAP1 mediates the disruption of adherens junctions to promote Escherichia coli K1 invasion of brain endothelial cells.Cell Microbiol. 2012 Sep;14(9):1415-33. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2012.01805.x. Epub 2012 May 24. Cell Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22519731 Free PMC article.
-
Current concepts on Escherichia coli K1 translocation of the blood-brain barrier.FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2004 Nov 1;42(3):271-9. doi: 10.1016/j.femsim.2004.09.001. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15477040 Review.
-
Invasion processes of pathogenic Escherichia coli.Int J Med Microbiol. 2005 Oct;295(6-7):463-70. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2005.07.004. Int J Med Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16238020 Review.
Cited by
-
Angiotensin II receptor type 1--a novel target for preventing neonatal meningitis in mice by Escherichia coli K1.J Infect Dis. 2014 Feb 1;209(3):409-19. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jit499. Epub 2013 Sep 16. J Infect Dis. 2014. PMID: 24041786 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid rafts and pathogens: the art of deception and exploitation.J Lipid Res. 2020 May;61(5):601-610. doi: 10.1194/jlr.TR119000391. Epub 2019 Oct 15. J Lipid Res. 2020. PMID: 31615838 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acinetobacter baumannii Outer Membrane Protein A Induces Pulmonary Epithelial Barrier Dysfunction and Bacterial Translocation Through The TLR2/IQGAP1 Axis.Front Immunol. 2022 Jun 30;13:927955. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.927955. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35844614 Free PMC article.
-
Host-pathogen interactions in bacterial meningitis.Acta Neuropathol. 2016 Feb;131(2):185-209. doi: 10.1007/s00401-015-1531-z. Epub 2016 Jan 7. Acta Neuropathol. 2016. PMID: 26744349 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resistance of the brain to Escherichia coli K1 infection depends on MyD88 signaling and the contribution of neutrophils and monocytes.Infect Immun. 2013 May;81(5):1810-9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01349-12. Epub 2013 Mar 11. Infect Immun. 2013. PMID: 23478323 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aletayeb MH, Ahmad FS, D Masood. An 11-year study of causes of neonatal bacterial meningitis in Ahvaz, Iran. Pediatr Int. 2010;52:463–466. - PubMed
-
- Banerjee PP, Vinay DS, Mathew A, Raje M, Parekh V, Prasad DV, et al. Evidence that glycoprotein 96 (B2), a stress protein, functions as a Th2-specific costimulatory molecule. J Immunol. 2002;169:3507–3518. - PubMed
-
- Carmody RJ, Chen YH. Nuclear factor-kappaB: activation and regulation during toll-like receptor signaling. Cell Mol Immunol. 2007;4:31–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

