Effect of different host plants on nutritional indices of the pod borer, Helicoverpa armigera
- PMID: 22963648
- PMCID: PMC3476957
- DOI: 10.1673/031.012.5501
Effect of different host plants on nutritional indices of the pod borer, Helicoverpa armigera
Abstract
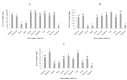
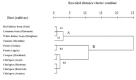
Nutritional indices of Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) on different host plants including chickpea (cultivars Arman, Hashem, Azad, and Binivich), common bean (cultivar Khomein), white kidney bean (cultivar Dehghan), red kidney bean (cultivar Goli), cowpea (cultivar Mashhad), tomato (cultivar Meshkin) and potato (cultivars Agria and Satina) were studied under laboratory conditions (25 ± 1 °C, 65 ± 5% RH, 16:8 L:D). Third instar larvae reared on potato Agria showed the highest efficiency of conversion of digested food (ECD) and efficiency of conversion of ingested food (ECI) (50.800 ± 0.104% and 13.630 ± 0.016%, respectively). Approximate digestibility (AD) values of the fourth instar larvae were highest (92.651 ± 0.004%) and lowest (57.140 - 0.049%) on chickpea Azad and potato Agria, respectively. The fifth instar larvae fed on tomato Meshkin and white kidney bean Dehghan had the highest consumption index (CI) (3.717 ± 0.091) and relative consumption rate (RCR) (1.620 ± 0.074), respectively. Whole larval instars showed the highest ECI and ECD values on potatoes Satina (14.640 ± 0.014%) and Agria (21.380 ± 0.015%), respectively, and the lowest of both values on tomato Meshkin (ECI: 5.748 ± 0.002% and ECD: 7.341 ± 0.002%). The results of nutritional indices and the cluster analysis indicated that tomato Meshkin was an unsuitable host for feeding of H. armigera.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nutritional performance and activity of some digestive enzymes of the cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera, in response to seven tested bean cultivars.J Insect Sci. 2014;14:93. doi: 10.1093/jis/14.1.93. J Insect Sci. 2014. PMID: 25368049 Free PMC article.
-
Digestive proteolytic and amylolytic activities and feeding responses of Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) on different host plants.J Econ Entomol. 2012 Aug;105(4):1439-46. doi: 10.1603/ec11345. J Econ Entomol. 2012. PMID: 22928327
-
Evaluation of artificial diets based on different legume seeds on the nutritional physiology and digestive function of Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner).Bull Entomol Res. 2023 Feb;113(1):133-143. doi: 10.1017/S0007485322000402. Epub 2022 Sep 6. Bull Entomol Res. 2023. PMID: 36065765
-
Nutritional performance of the tomato fruit borer, Helicoverpa armigera, on different tomato cultivars.J Insect Sci. 2014;14:102. doi: 10.1673/031.014.102. J Insect Sci. 2014. PMID: 25204681 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding heliothine (Lepidoptera: Heliothinae) pests: what is a host plant?J Econ Entomol. 2014 Jun;107(3):881-96. doi: 10.1603/ec14036. J Econ Entomol. 2014. PMID: 25026644 Review.
Cited by
-
Nutritional performance and activity of some digestive enzymes of the cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera, in response to seven tested bean cultivars.J Insect Sci. 2014;14:93. doi: 10.1093/jis/14.1.93. J Insect Sci. 2014. PMID: 25368049 Free PMC article.
-
Growth and nutrition of Agelastica coerulea (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) larvae changed when fed with leaves obtained from an O3-enriched atmosphere.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018 May;25(13):13186-13194. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-1683-1. Epub 2018 Mar 10. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29525869
-
Midgut serine proteinases participate in dietary adaptations of the castor (Eri) silkworm Samia ricini Anderson transferred from Ricinus communis to an ancestral host, Ailanthus excelsa Roxb.Front Insect Sci. 2023 Aug 10;3:1169596. doi: 10.3389/finsc.2023.1169596. eCollection 2023. Front Insect Sci. 2023. PMID: 38469493 Free PMC article.
-
Does Larval Rearing Diet Lead to Premating Isolation in Spodoptera litura (Fabricius) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae)?Insects. 2021 Feb 27;12(3):203. doi: 10.3390/insects12030203. Insects. 2021. PMID: 33673724 Free PMC article.
-
Biotic Potential and Life Table of Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) from Three Brazilian Regions.Neotrop Entomol. 2018 Jun;47(3):344-351. doi: 10.1007/s13744-017-0529-8. Epub 2017 May 8. Neotrop Entomol. 2018. PMID: 28484967
References
-
- Anonymous. Crop Protection Compendium. 2nd Edition. CAB-International; 2000. Helicoverpa armigera Hübner. CD-ROM.
-
- Arghand A, Naseri B, Razmjou J, Hassanpour M. Feeding indices of the cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) on seed of five different maize hybrids. Global Conference on Entomology; Chiang Mai, Thailand: 2011. March 5–9, 2011.
-
- Ashfaq M, Ahmad KJ, Ali A. Morphophysical factors affecting consumption and coefficient of utilization of Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner). Pakistan Journal of Applied Sciences. 2003;3:225–230.
-
- Banerjee MK, Kalloo G. Role of phenols in resistance to tomato leaf curl virus, Fusarium wilt and fruit borer in Lycopersicon. . Current Science. 1989;58:575–576.
-
- Barton Browne L. Ontogenetic changes in feeding behavior. In: Chapman RF, de Boer G, editors. Regulatory Mechanisms in Insect Feeding. Chapman and Hall; 1995. pp. 307–342.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

