Interactions between modafinil and cocaine during the induction of conditioned place preference and locomotor sensitization in mice: implications for addiction
- PMID: 22963989
- PMCID: PMC4528911
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbr.2012.07.039
Interactions between modafinil and cocaine during the induction of conditioned place preference and locomotor sensitization in mice: implications for addiction
Abstract
Modafinil is a wake-promoting drug effective at enhancing alertness and attention with a variety of approved and off-label applications. The mechanism of modafinil is not well understood but initial studies indicated a limited abuse potential. A number of recent publications, however, have shown that modafinil can be rewarding under certain conditions. The present study assessed the reinforcing properties of modafinil using conditioned place preference and locomotor sensitization in mice. Experiment 1 examined a high dose of modafinil (75 mg/kg) as well as its interactions with cocaine (15 mg/kg). Cocaine alone and modafinil co-administered with cocaine induced sensitization of locomotor activity; modafinil alone showed little or no locomotor sensitization. Animals given modafinil alone, cocaine alone, and modafinil plus cocaine exhibited a strong and roughly equivalent place preference. When tested for sensitization using a low challenge dose of modafinil, cross-sensitization was observed in all cocaine-pretreated mice. Experiment 2 examined a low dose of modafinil that is similar to the dose administered to humans and has been shown to produce cognitive enhancements in mice. Low dose modafinil (0.75 mg/kg) did not produce conditioned place preference or locomotor sensitization. Together, these results suggest that modafinil has the potential to produce reward, particularly in cocaine addicts, and should be used with caution. However, the typical low dose administered likely moderates these effects and may account for lack of addiction seen in humans.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest and did not receive funding from the makers of modafinil.
Figures
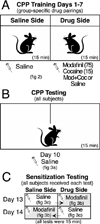
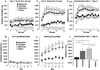

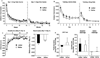
References
-
- Bastuji H, Jouvet M. Successful treatment of idiopathic hypersomnia and narcolepsy with modafinil. Progress in Neuropsychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry. 1988;12:695–700. - PubMed
-
- Cephalon FDA Approved Labeling Text for NDA 20-717/S-005 & S008. Provigil® (modafinil) Tablets [C-IV] 2004 Approved 23-Jan-2004.
-
- O’Connor A. Wakefulness finds a powerful ally. New York Times. 2004
-
- Beracochea D, Celerier A, Peres M, Pierard C. Enhancement of learning processes following an acute modafinil injection in mice. Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior. 2003;76:473–479. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

