Project həli?dx(w)/Healthy Hearts Across Generations: development and evaluation design of a tribally based cardiovascular disease prevention intervention for American Indian families
- PMID: 22965622
- PMCID: PMC3505854
- DOI: 10.1007/s10935-012-0274-z
Project həli?dx(w)/Healthy Hearts Across Generations: development and evaluation design of a tribally based cardiovascular disease prevention intervention for American Indian families
Abstract
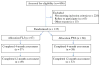
American Indian and Alaska Native (AIAN) populations are disproportionately at risk for cardiovascular disease (CVD), diabetes, and obesity, compared with the general US population. This article describes the həli?dx(w)/Healthy Hearts Across Generations project, an AIAN-run, tribally based randomized controlled trial (January 2010-June 2012) designed to evaluate a culturally appropriate CVD risk prevention program for AI parents residing in the Pacific Northwest of the United States. At-risk AIAN adults (n = 135) were randomly assigned to either a CVD prevention intervention arm or a comparison arm focusing on increasing family cohesiveness, communication, and connectedness. Both year-long conditions included 1 month of motivational interviewing counseling followed by personal coach contacts and family life-skills classes. Blood chemistry, blood pressure, body mass index, food intake, and physical activity were measured at baseline and at 4- and 12-month follow-up times.
References
-
- Archer SL, Greenlund KJ, Valdez R, Casper ML, Rith-Najarian S, Croft JB. Differences in food habits and cardiovascular disease risk among Native Americans with and without diabetes: The Inter-Tribal Heart Project. Public Health Nutrition. 2004;7:1025–1032. - PubMed
-
- Australian Bureau of Statistics. Nutrient Intakes and physical measurements. Canberra, Australia: Australian Bureau of Statistics; 1998. Report No. 4805.0.
-
- Birch LL, Fisher JO, Grimm-Thomas K, Markey CN, Sawyer R, Johnson SL. Confirmatory factor analysis of the Child Feeding Questionnaire: A measure of parental attitudes, beliefs and practices about child feeding and obesity proneness. Appetite. 2001;36:201–210. - PubMed
-
- Bland M. An introduction to medical statistics. 3. Oxford, England: Oxford University Press; 2000.
-
- Bryant MJ, Ward DS, Hales D, Vaughn A, Tabak RG, Stevens J. Reliability and validity of the Healthy Home Survey: A tool to measure factors within homes hypothesized to relate to overweight in children. The International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity. 2008;5:23. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical